409510
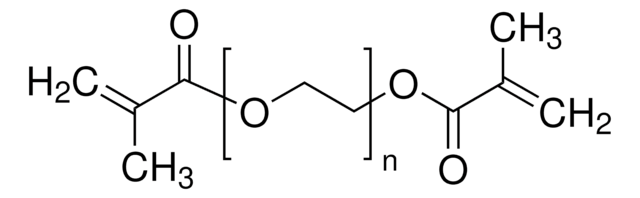
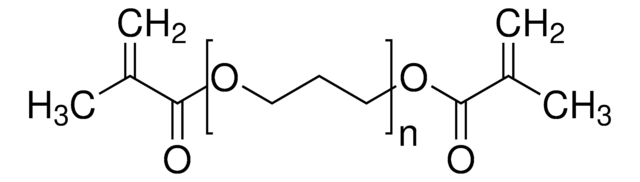
Poly(ethylene glycol) dimethacrylate
average MN 550, cross-linking reagent polymerization reactions, methacrylate, 80-120 ppm MEHQ as inhibitor, 270-330 ppm BHT as inhibitor
Synonyme(s) :
Polyethylene glycol, PEG dimethacrylate
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Nom du produit
Poly(ethylene glycol) dimethacrylate, average Mn 550, contains 80-120 ppm MEHQ as inhibitor, 270-330 ppm BHT as inhibitor
Forme
liquid
Niveau de qualité
Poids mol.
average Mn 550
Contient
270-330 ppm BHT as inhibitor
80-120 ppm MEHQ as inhibitor
Pertinence de la réaction
reagent type: cross-linking reagent
reaction type: Polymerization Reactions
Indice de réfraction
n20/D 1.466
pb
>200 °C/2 mmHg (lit.)
Densité
1.099 g/mL at 25 °C
Extrémité Ω
methacrylate
Extrémité α
methacrylate
Architecture des polymères
shape: linear
functionality: homobifunctional
Température de stockage
2-8°C
Chaîne SMILES
OCCO.CC(=C)C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C10H14O4/c1-7(2)9(11)13-5-6-14-10(12)8(3)4/h1,3,5-6H2,2,4H3
Clé InChI
STVZJERGLQHEKB-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Application
- PDGF-AA loaded photo-crosslinked chitosan-based hydrogel for promoting wound healing.: This study investigates the use of a chitosan-based hydrogel, photo-crosslinked with Poly(ethylene glycol) dimethacrylate (PEGDMA), to deliver PDGF-AA and enhance wound healing. The results demonstrate significant improvements in wound closure rates and tissue regeneration (Cai et al., 2024).
- Reducing the foreign body response on human cochlear implants and their materials in vivo with photografted zwitterionic hydrogel coatings.: This research explores the application of PEGDMA in zwitterionic hydrogel coatings to minimize foreign body responses in cochlear implants. The coatings significantly reduced inflammation and improved biocompatibility in vivo (Horne et al., 2023).
- Full factorial design of experiment-based and response surface methodology approach for evaluating variation in uniaxial compressive mechanical properties, and biocompatibility of photocurable PEGDMA-based scaffolds.: This study uses a full factorial design to optimize the mechanical properties and biocompatibility of PEGDMA-based scaffolds, highlighting their potential use in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine (Bharadwaz et al., 2023).
- Antifouling and Mechanical Properties of Photografted Zwitterionic Hydrogel Thin-Film Coatings Depend on the Cross-Link Density.: This article examines how varying the cross-link density in PEGDMA-based hydrogel coatings affects their antifouling and mechanical properties. The findings are relevant for the development of durable and biocompatible medical device coatings (Jensen et al., 2021).
- Biocompatible and photocrosslinkable poly(ethylene glycol)/keratin biocomposite hydrogels.: The research presents the development of PEGDMA/keratin biocomposite hydrogels, demonstrating excellent biocompatibility and potential applications in drug delivery systems and tissue engineering (Wang et al., 2021).
Code de la classe de stockage
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 1
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Articles
In this article, we will discuss the benefits and limitations of several 2D and 3D scaffold patterning techniques that can be applied in the presence of cells. Although these methods will be discussed in the context of poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG)-based hydrogels, they can technically be applied to any optically transparent, photoactive substrate.
Progress in biotechnology fields such as tissue engineering and drug delivery is accompanied by an increasing demand for diverse functional biomaterials. One class of biomaterials that has been the subject of intense research interest is hydrogels, because they closely mimic the natural environment of cells, both chemically and physically and therefore can be used as support to grow cells. This article specifically discusses poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) hydrogels, which are good for biological applications because they do not generally elicit an immune response. PEGs offer a readily available, easy to modify polymer for widespread use in hydrogel fabrication, including 2D and 3D scaffold for tissue culture. The degradable linkages also enable a variety of applications for release of therapeutic agents.
Devising biomaterial scaffolds that are capable of recapitulating critical aspects of the complex extracellular nature of living tissues in a threedimensional (3D) fashion is a challenging requirement in the field of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique