406996
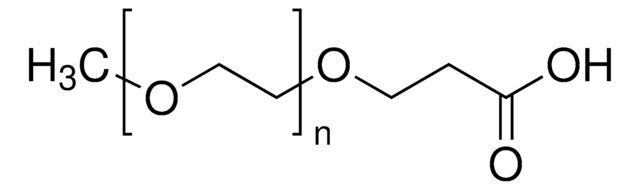
Poly(ethylene glycol) bis(carboxymethyl) ether
average MN 250, cross-linking reagent amine reactive, carboxylic acid
Synonyme(s) :
Polyethylene glycol, Polyethylene glycol 250 diacid, Polyglycol 250 diacid
About This Item
Produits recommandés
product name
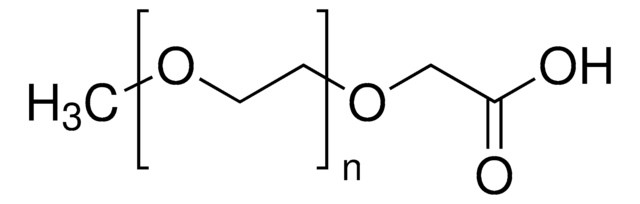
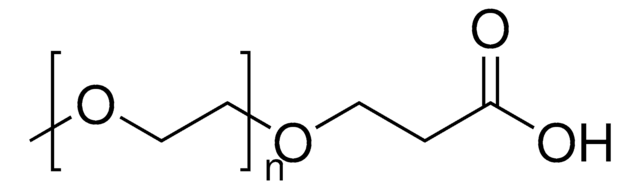
Poly(ethylene glycol) bis(carboxymethyl) ether, average Mn 250
Forme
viscous liquid
Poids mol.
average Mn 250
Pertinence de la réaction
reagent type: cross-linking reagent
reactivity: amine reactive
Indice de réfraction
n20/D 1.454
Densité
1.302 g/mL at 25 °C
Extrémité Ω
carboxylic acid
Extrémité α
carboxylic acid
Architecture des polymères
shape: linear
functionality: homobifunctional
Chaîne SMILES
OCCO.OCC(O)=O
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Description générale
Application
Code de la classe de stockage
10 - Combustible liquids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 1
Point d'éclair (°F)
572.0 °F - closed cup
Point d'éclair (°C)
300 °C - closed cup
Équipement de protection individuelle
Faceshields, Gloves, Goggles, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Articles
Progress in biotechnology fields such as tissue engineering and drug delivery is accompanied by an increasing demand for diverse functional biomaterials. One class of biomaterials that has been the subject of intense research interest is hydrogels, because they closely mimic the natural environment of cells, both chemically and physically and therefore can be used as support to grow cells. This article specifically discusses poly(ethylene glycol) (PEG) hydrogels, which are good for biological applications because they do not generally elicit an immune response. PEGs offer a readily available, easy to modify polymer for widespread use in hydrogel fabrication, including 2D and 3D scaffold for tissue culture. The degradable linkages also enable a variety of applications for release of therapeutic agents.
Devising biomaterial scaffolds that are capable of recapitulating critical aspects of the complex extracellular nature of living tissues in a threedimensional (3D) fashion is a challenging requirement in the field of tissue engineering and regenerative medicine.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique



![2-[2-(2-Methoxyethoxy)ethoxy]acetic acid technical grade](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/335/694/b58c539b-141f-4ab2-98d9-5f46c748490b/640/b58c539b-141f-4ab2-98d9-5f46c748490b.png)