274135
N,N-Dimethylacrylamide
99%, contains 500 ppm monomethyl ether hydroquinone as inhibitor
Synonyme(s) :
2-Propenamide
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Niveau de qualité
Pureté
99%
Forme
liquid
Contient
500 ppm monomethyl ether hydroquinone as inhibitor
Indice de réfraction
n20/D 1.473 (lit.)
Point d'ébullition
80-81 °C/20 mmHg (lit.)
Densité
0.962 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
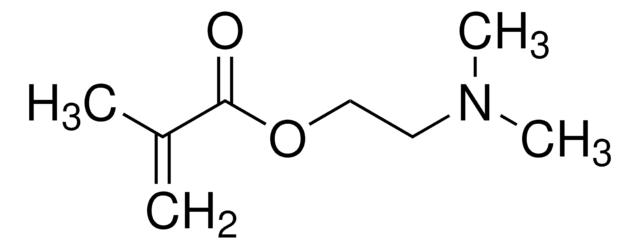
Chaîne SMILES
CN(C)C(=O)C=C
InChI
1S/C5H9NO/c1-4-5(7)6(2)3/h4H,1H2,2-3H3
Clé InChI
YLGYACDQVQQZSW-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Description générale
Application
- Synthesis of poly(N,N-dimethylacrylamide) (PDMAA) nanoparticles which are used in biomedical and drug delivery applications.
- Use as a co-monomer in the synthesis of thermoresponsive polymers used in smart coatings, adhesives, and sensors.
- As a reactive diluent in the manufacture of UV-cured coatings and inks.
- Use as a co-monomer with polyethylene glycol dimethacrylate (PEGDMA) and a chitosan derivative to develop an injectable hydrogel that can be used as a bone tissue engineering matrix.
- A series of DMMA-based hydrogels for the removal of heavy metals and organic dyes from polluted water. These hydrogels are highly efficient in removing cationic dyes due to electrostatic interaction and hydrogen bonding in the DMMA backbone.
- Non-toxic luminescent carbon dot/poly(DMMA) nanocomposite via surface-initiated reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization.
- Polymer coating for quartz crystal microbalance(QCM) sensor. The poly(DMMA) gel acts as a sensing material to adsorb Au(III) ions from HCl aqueous solution and it is inactive to most other metal ions and organic compounds.
Caractéristiques et avantages
- It is an appropriate precursor for copolymerization due to its low initiation temperature and high reactivity.
- Its unique structure forms a 3D network and improves the water retention capacity of hydrogels.
- It is highly soluble in water.
- It can easily bind to colloidal particles to enhance the bridging effect which plays a key role in flocculation.
Mention d'avertissement
Danger
Mentions de danger
Conseils de prudence
Classification des risques
Acute Tox. 3 Dermal - Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Eye Dam. 1
Code de la classe de stockage
6.1C - Combustible acute toxic Cat.3 / toxic compounds or compounds which causing chronic effects
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
WGK 1
Point d'éclair (°F)
158.0 °F
Point d'éclair (°C)
70 °C
Équipement de protection individuelle
Eyeshields, Faceshields, Gloves, type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Les clients ont également consulté
Articles
The manufacture of monomers for use in ophthalmic applications is driven by the need for higher purity, improved reliability of manufacturing supply, but ultimately by the need for the increased comfort, convenience, and safety of contact lens wearers. Daily wear contact lenses have the potential to fill this need for many customers; however, their widespread use is constrained by higher costs compared to weekly- or monthly-based lenses. New approaches that improve cost structure and result in higher quality raw materials are needed to help make contact lenses more affordable and accelerate growth of the contact lens market.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique





![N-[3-(Dimethylamino)propyl]methacrylamide 99%, contains MEHQ as inhibitor](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/295/145/6b4aae15-7cb5-4b7b-9c06-8e6d24e50951/640/6b4aae15-7cb5-4b7b-9c06-8e6d24e50951.png)
![3-[Tris(trimethylsiloxy)silyl]propyl methacrylate contains MEHQ + HQ as stabilizer, 98%](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/148/664/33ff5116-f264-4a64-824a-009c2ca5b2b3/640/33ff5116-f264-4a64-824a-009c2ca5b2b3.png)