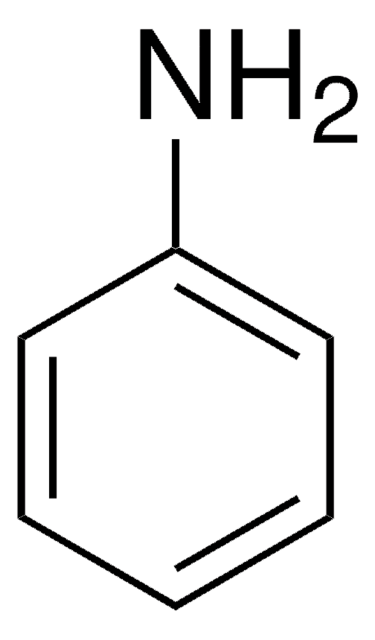
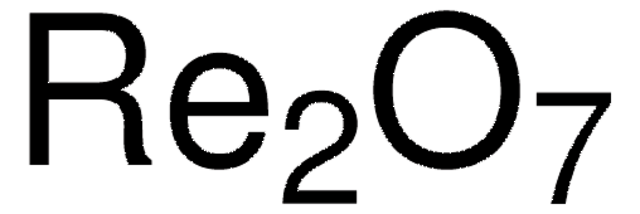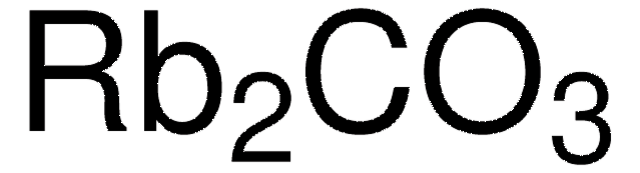267317
Rhenium
foil, thickness 0.25 mm, 99.98% trace metals basis
Synonyme(s) :
Rhenium element
About This Item
Produits recommandés
Niveau de qualité
Pureté
99.98% trace metals basis
Forme
foil
Description
19.3 μΩ-cm, 20°C
Épaisseur
0.25 mm
Point d'ébullition
5596 °C (lit.)
5627 °C (lit.)
Pf
3180 °C (lit.)
Densité
21.02 g/cm3 (lit.)
Chaîne SMILES
[ReH]
InChI
1S/Re
Clé InChI
WUAPFZMCVAUBPE-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Vous recherchez des produits similaires ? Visite Guide de comparaison des produits
Catégories apparentées
Description générale
Application
It can be used as an additive to prepare a molybdenum-titanium-zirconium (TZM) alloy joint to improve its tensile strength.
It can also be used as a catalyst for various hydrodeoxygenation reactions.
Quantité
Code de la classe de stockage
13 - Non Combustible Solids
Classe de danger pour l'eau (WGK)
nwg
Point d'éclair (°F)
Not applicable
Point d'éclair (°C)
Not applicable
Équipement de protection individuelle
Eyeshields, Gloves, type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges
Faites votre choix parmi les versions les plus récentes :
Déjà en possession de ce produit ?
Retrouvez la documentation relative aux produits que vous avez récemment achetés dans la Bibliothèque de documents.
Articles
Can there be an effective strategy for finding breakthrough materials, since they are, by definition, unpredictable? One answer is found in Combinatorial Materials Science techniques, which represent a powerful approach to identifying new and unexpected materials.
Notre équipe de scientifiques dispose d'une expérience dans tous les secteurs de la recherche, notamment en sciences de la vie, science des matériaux, synthèse chimique, chromatographie, analyse et dans de nombreux autres domaines..
Contacter notre Service technique