V900887
Proteinase K from Tritirachium album
Vetec™, reagent grade, powder, ≥30 units/mg protein
Synonym(s):
Endopeptidase K
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
CAS Number:
EC Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
Recommended Products
grade
reagent grade
product line
Vetec™
form
powder
specific activity
≥30 units/mg protein
mol wt
28.93 kDa
technique(s)
DNA extraction: suitable
foreign activity
Dnase ≤30 units/mg solid
storage temp.
−20°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Application
Useful for the proteolytic inactivation of nucleases during the isolation of DNA and RNA.
Removes endotoxins that bind to cationic proteins such as lysozyme and ribonuclease A.
Reported useful for the isolation of hepatic, yeast, and mung bean mitochondria
Determination of enzyme localization on membranes
Treatment of paraffin embedded tissue sections to expose antigen binding sites for antibody labeling.
Digestion of proteins from brain tissue samples for prions in Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathies (TSE) research.
Removes endotoxins that bind to cationic proteins such as lysozyme and ribonuclease A.
Reported useful for the isolation of hepatic, yeast, and mung bean mitochondria
Determination of enzyme localization on membranes
Treatment of paraffin embedded tissue sections to expose antigen binding sites for antibody labeling.
Digestion of proteins from brain tissue samples for prions in Transmissible Spongiform Encephalopathies (TSE) research.
Biochem/physiol Actions
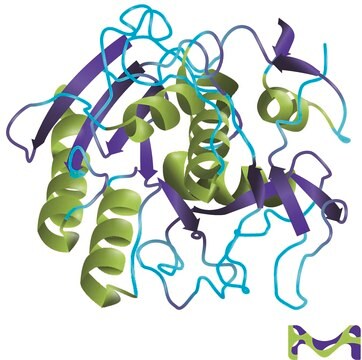
Proteinase K is a stable and highly reactive serine protease. Evidence from crystal and molecular structure studies indicates the enzyme belongs to the subtilisin family with an active-site catalytic triad (Asp39-His69-Ser224). It is stable in a broad range of environments: pH, buffer salts, detergents (SDS), and temperature. In the presence of 0.1-0.5% SDS, proteinase K retains activity and will digest a variety of proteins and nucleases in DNA preparations without compromising the integrity of the isolated DNA.
Unit Definition
One unit will hydrolyze urea denatured hemoglobin to produce color equivalent to 1.0 micromole of tyrosine per minute at pH 7.5 at 37 deg C.
Legal Information
Vetec is a trademark of Merck KGaA, Darmstadt, Germany
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Yan-Fang Xian et al.
Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity, 2020, 5920476-5920476 (2020-07-28)
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is a common neurodegenerative disease characterized by progressive memory loss. Magnolol (MN), the main active ingredient of Magnolia officinalis, possesses anti-AD effects in several experimental models of AD. In this study, we aimed to explore whether MN
Shuangshuo Jia et al.
Frontiers in cell and developmental biology, 10, 797855-797855 (2022-04-01)
Irisin, a myokine secreted by muscle during physical exercise, is known to have biological activities in different cell types. Chondrocyte inflammation and pyroptosis have been shown to play important roles in osteoarthritis (OA). In this study, we investigated the effects
Hui-Qin Li et al.
Brain, behavior, and immunity, 82, 264-278 (2019-09-03)
Isorhynchophylline (IRN) has been demonstrated to have distinct anti-Alzheimer's disease (AD) activity in several animal models of AD. In this study, we aimed at evaluating the preventive effect of IRN on the cognitive deficits and amyloid pathology in TgCRND8 mice.
Yi-sheng Chen et al.
Archives of microbiology, 196(3), 193-199 (2014-02-05)
Lactobacillus plantarum 510, previously isolated from a koshu vineyard in Japan, was found to produce a bacteriocin-like inhibitory substance which was purified and characterized. Mass spectrometry analysis showed that the mass of this bacteriocin is 4,296.65 Da. A partial sequence, NH2-
Neetu Kumra Taneja et al.
Journal of bacteriology, 195(22), 5102-5111 (2013-09-10)
Bordetella pertussis is the causative agent of pertussis, a highly contagious disease of the human respiratory tract. Despite very high vaccine coverage, pertussis has reemerged as a serious threat in the United States and many developing countries. Thus, it is
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service