V4762
Monoclonal Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Receptor-1 antibody produced in mouse
clone FLT-19, tissue culture supernatant
Synonym(s):
Anti-Flt1 Receptor, Anti-VEGF R-1
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
Quality Level
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
tissue culture supernatant
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
FLT-19, monoclonal
contains
15 mM sodium azide
species reactivity
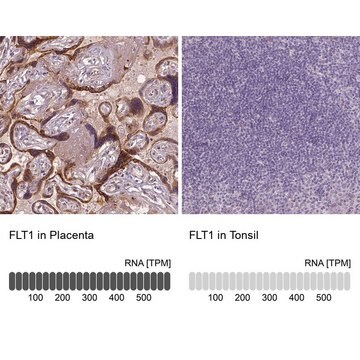
human
technique(s)
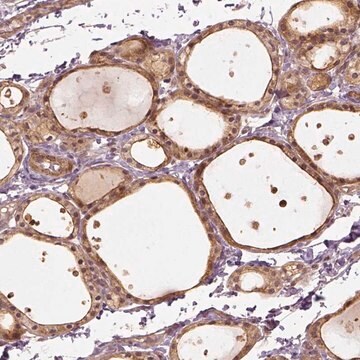
immunohistochemistry (frozen sections): 1:100 using human placenta
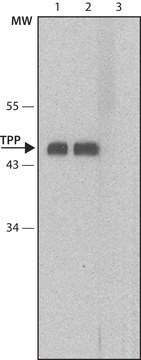
immunoprecipitation (IP): suitable
indirect ELISA: suitable
microarray: suitable
isotype
IgG1
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
human ... FLT1(2321)
General description
Immunogen
Application
- immunofluorescence labelling
- enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA)
- immunohistochemistry
- immunoprecipitation
Biochem/physiol Actions
Disclaimer
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
STOT RE 2
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service