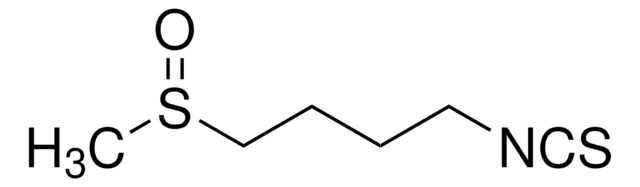
S5519
Lipoprotein Deficient Serum from human plasma
sterile-filtered, frozen liquid
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352202
NACRES:
NA.26
biological source:
human
origin:
USA origin
sterility:
sterile-filtered
form:
frozen liquid
shipped in:
dry ice
Recommended Products
biological source
human
Quality Level
sterility
sterile-filtered
form
frozen liquid
quality
No banding correlating to lipoprotein observed by Agarose Electrophoresis
composition
protein, ≥50 mg/mL biuret
origin
USA origin
concentration
≥50 mg protein/mL Biuret
technique(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
Gene Information
human ... APOA1(335) , APOA4(337) , APOA5(116519) , APOB(338) , APOC1(341) , APOC3(345) , APOE(348)
Biochem/physiol Actions
Lipoprotein deficient serum was shown to inhibit the transfer of unesterified cholesterol from LDL to HDL.
Preparation Note
Dialyzed against Dulbecco′s phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.2-7.3
Disclaimer
RESEARCH USE ONLY. This product is regulated in France when intended to be used for scientific purposes, including for import and export activities (Article L 1211-1 paragraph 2 of the Public Health Code). The purchaser (i.e. enduser) is required to obtain an import authorization from the France Ministry of Research referred in the Article L1245-5-1 II. of Public Health Code. By ordering this product, you are confirming that you have obtained the proper import authorization.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
E Velazquez et al.
Biomedica biochimica acta, 50(9), 1109-1114 (1991-01-01)
The in vitro transfer of radiolabelled unesterified cholesterol from human low- and very low- to high-density lipoproteins in the presence of either lipoprotein deficient serum or bovine serum albumin has been studied. The rate of transfer was faster from LDL
Inés Pineda Torra et al.
Molecular and cellular biology, 28(8), 2626-2636 (2008-02-06)
Dysregulation of liver X receptor alpha (LXRalpha) activity has been linked to cardiovascular and metabolic diseases. Here, we show that LXRalpha target gene selectivity is achieved by modulation of LXRalpha phosphorylation. Under basal conditions, LXRalpha is phosphorylated at S198; phosphorylation
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service