S2147
Monoclonal Anti-Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) antibody produced in mouse
clone SD-G6, ascites fluid
Synonym(s):
Anti-ALS, Anti-ALS1, Anti-HEL-S-44, Anti-IPOA, Anti-SOD, Anti-STAHP, Anti-hSod1, Anti-homodimer
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
Quality Level
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
ascites fluid
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
SD-G6, monoclonal
contains
15 mM sodium azide
species reactivity
canine, human, rat
technique(s)
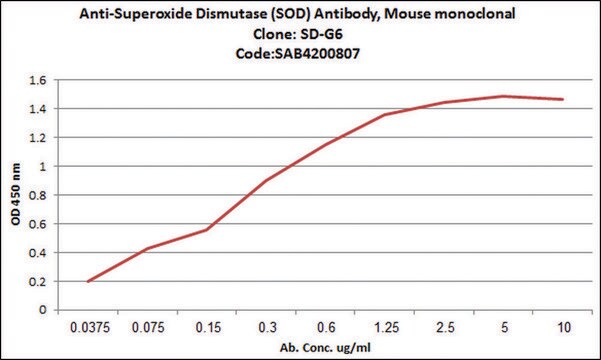
indirect ELISA: 1:300
isotype
IgG1
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
human ... SOD1(6647)
rat ... Sod1(24786)
General description
Monoclonal Anti-Superoxide Dismutase (mouse IgG1 isotype) is derived from the hybridoma produced by the fusion of mouse myeloma cells and splenocytes from an immunized mouse. Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) is a family of metalloenzymes widely distributed in both plants and animals. In mammalian tissues, three types of superoxide dismutase [Cu-Zn-SOD, Mn-SOD, extracellular (EC)-SOD] occur. Human manganese superoxide dismutase (MnSOD), isolated from liver is composed of 22 kDa subunits each containing one Mn atom, while SOD from bovine erythrocyte has a molecular weight of 32.5 kDa. Superoxide Dismutase occurs in high concentrations in brain, liver, heart, erythrocytes and kidney.
Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) or CuZn-SOD (SOD1), a cytoplasmic and mitochondrial intermembrane space protein is located on human chromosome 21q22. It belongs to superoxide dismutase multigene family.
Specificity
The antibody recognizes natural and recombinant human-Cu-Zn-SOD, human placental SOD, and human erythrocyte SOD using direct capture or competitive ELISA. Cross-reactivity has been observed with human liver and salivary gland, rat salivary gland, pheochromocytoma cell line (PC12), and dog salivary gland. No reactivity was observed with SOD from bovine erythrocytes, kidney, and liver; dog erythrocytes; Bacillus stearothermophilus; E. coli, or horseradish.
Immunogen
recombinant human copper-zinc superoxide dismutase (Cu-Zn-SOD).
Application
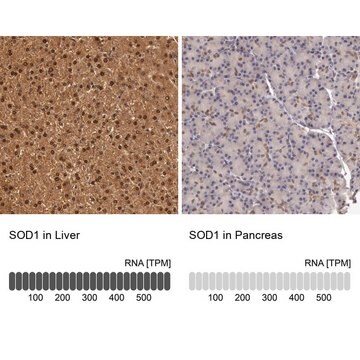
Anti-Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) antibody has been used in immunohistochemistry and Cu-Zn SOD detection via ELISA.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) appear to protect cells against reactive free radicals by scavenging the superoxide radicals produced by ionization radiation or through other mechanisms. SOD have been proposed as clinically useful for a wide variety of applications including prevention of oncogenesis, tumor promotion, tumor invasiveness, radiation damage, reduction of the cytotoxic and cardiotoxic effects of anticancer drugs, as a measure against the aging process and as anti-inflammatory agents.
Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) or CuZn-SOD (SOD1) mutations results in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis It acts as a mediator of the HMF (hypomagnetic field) effect.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) and response of antioxidants as ROS-scavengers during environmental stress in plants
Das K, et al.
Frontiers in environmental science., 2 (2014)
Formation of high molecular weight complexes of mutant Cu, Zn-superoxide dismutase in a mouse model for familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Johnston JA, et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the USA, 97(23), 12571-12576 (2000)
Superoxide dismutase multigene family: a comparison of the CuZn-SOD (SOD1), Mn-SOD (SOD2), and EC-SOD (SOD3) gene structures, evolution, and expression
Zelko IN, et al.
Free Radical Biology & Medicine, 33(3), 337-349 (2002)
J A Johnston et al.
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97(23), 12571-12576 (2000-10-26)
Deposition of aggregated protein into neurofilament-rich cytoplasmic inclusion bodies is a common cytopathological feature of neurodegenerative disease. How-or indeed whether-protein aggregation and inclusion body formation cause neurotoxicity are presently unknown. Here, we show that the capacity of superoxide dismutase (SOD)
Marcel Maier et al.
Science translational medicine, 10(470) (2018-12-07)
Mutations in the gene encoding superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) lead to misfolding and aggregation of SOD1 and cause familial amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (FALS). However, the implications of wild-type SOD1 misfolding in sporadic forms of ALS (SALS) remain unclear. By screening
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service