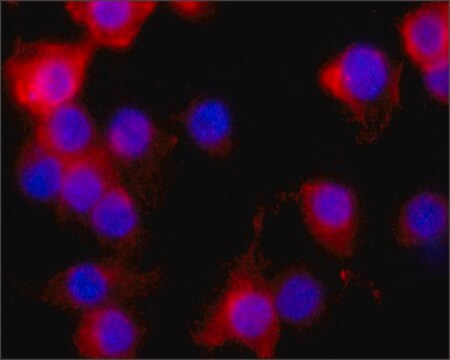
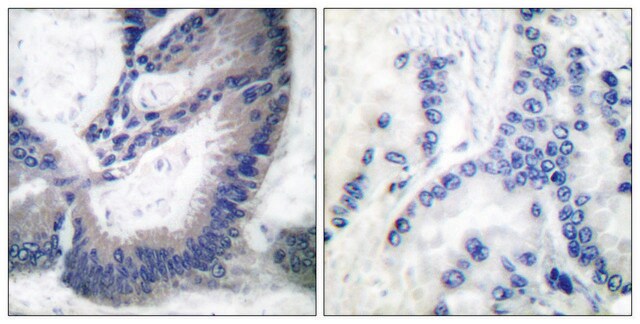
N7280
Anti-Nitric Oxide Synthase, Brain (1409-1429) antibody produced in rabbit
IgG fraction of antiserum, buffered aqueous solution
Synonym(s):
Anti-bNOS
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
rabbit
Quality Level
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
IgG fraction of antiserum
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
polyclonal
form
buffered aqueous solution
mol wt
antigen 150-160 kDa
species reactivity
rat
technique(s)
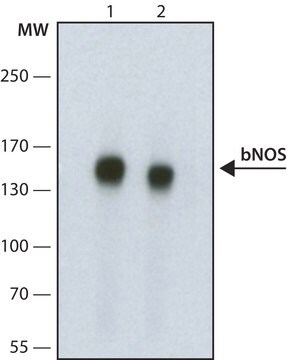
western blot: 1:10,000 using rat brain extract
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Gene Information
human ... NOS1(4842)
rat ... Nos1(24598)
General description
In humans, nitric oxide synthase 1 (NOS1) or neuronal nitric acid synthase (nNOS) is localized to the sarcoplasmic reticulum. The gene encoding it is, localized on human chromosome 12q24.22. In rats, the protein is present in perivascular nerves supplying the cerebral vasculature. The gene encoding it is localized on rat chromosome 12q16.
The nitric oxide synthase (NOS) isoform found in neurons is a 150-160 kDa protein. It is also termed brain NOS, NOS1, neuronal NOS (nNOS or bNOS, neuronal constitutive NOS or Ca2+-regulated NOS (cNOS, ncNOS). The nNOS or NOS1 gene is mapped to human chromosome 12q24.22. bNOS is present in skeletal muscle, central, peripheral neurons and neuronal cell bodies. Human bNOS and endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) share 52% amino acid identity, and rat and human bNOS share 93% amino acid identity. Structurally NOS exists as homodimers. The N-terminal region comprises heme and calmodulin binding sites. The reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) and flavins binding regions are localized in C-terminal region.
Specificity
The antibody is specific for nitric oxide synthase (NOS) derived from brain. It does not recognize NOS derived from activated macrophages (iNOS) and endothelial cells (eNOS).
Immunogen
synthetic peptide corresponding to nitric oxide synthase (NOS) of rat brain origin (bNOS, amino acids 1409-1429) conjugated to KLH. The immunogen sequence differs from the human bNOS by a single amino acid residue.
Application
Anti-Nitric Oxide Synthase, Brain (1409-1429) antibody produced in rabbit has been used in:
- immunoblotting
- immunostaining
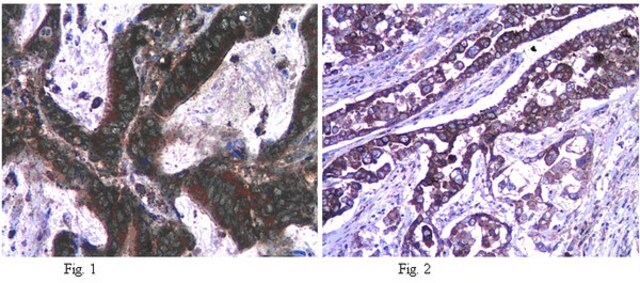
- immunohistochemistry
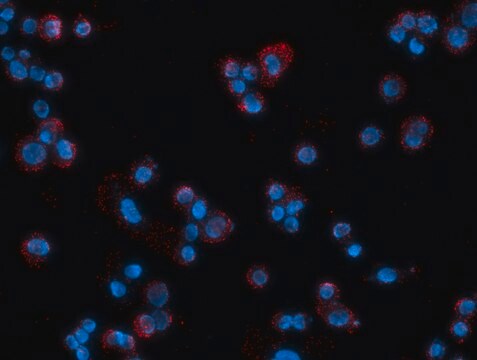
- immunofluorescence
- immunocytochemistry
Biochem/physiol Actions
Nitric oxide synthase (NOS), brain (nNOS or bNOS) mediates long-term regulation of synaptic transmission (long-term potentiation, long-term inhibition). It catalyzes the production of nitric oxide (NO) from L-arginine. The NO mediates neurovascular coupling and is associated with neuronal plasticity and pain signal transmission. nNOS regulates blood pressure, relaxation of smooth muscle and vasodilatation via peripheral nitrergic nerves. nNOS is complexed to dystrophin. However, in Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD), the skeletal muscle sarcolemma is devoid of nNOS.
Physical form
Solution in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4, containing 15 mM sodium azide
Storage and Stability
Store at 2-8 °C for up to one month. For extended storage, solution may be frozen in working aliquots. Repeated freezing and thawing, or storage in "frost-free" freezers,is not recommended. If slight turbidity occurs upon prolonged storage, clarify by centrifugation before use.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Selective synaptic cadherin expression by traced neurons of the chicken visual system
Dominik Heyers
The Journal of Neuroscience (2004)
Kristi A Kohlmeier et al.
Frontiers in neuroscience, 7, 246-246 (2014-01-07)
Orexin neuropeptides influence multiple homeostatic functions and play an essential role in the expression of normal sleep-wake behavior. While their two known receptors (OX1 and OX2) are targets for novel pharmacotherapeutics, the actions mediated by each receptor remain largely unexplored.
Integrated genome-wide association study findings: identification of a neurodevelopmental network for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder
Geert Poelmans
The American Journal of Psychiatry (2011)
Michael Leist et al.
Scientific reports, 6, 24904-24904 (2016-04-29)
Although hyperpolarization-activated cyclic nucleotide-gated cation (HCN) channels and the corresponding h-current (Ih) have been shown to fundamentally shape the activity pattern in the thalamocortical network, little is known about their function in local circuit GABAergic interneurons (IN) of the dorsal
Kinga Gzielo et al.
Cellular and molecular neurobiology, 37(5), 783-789 (2016-08-20)
Obesity in humans is associated with cognitive decline and elevated risk of neurodegenerative diseases of old age. Variations of high-fat diet are often used to model these effects in animal studies. However, we previously reported improvements in markers of memory
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service