G4387
L-Glutamic Dehydrogenase (NADP) from Proteus sp.
buffered aqueous solution, ≥4,000 units/mL
Synonym(s):
L-Glutamate:NADP+ oxidoreductase (deaminating)
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(6)
About This Item
CAS Number:
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
NACRES:
NA.54
Recommended Products
biological source
bacterial (Proteus spp.)
Quality Level
form
buffered aqueous solution
specific activity
≥4,000 units/mL
mol wt
~300 kDa
storage temp.
2-8°C
Application
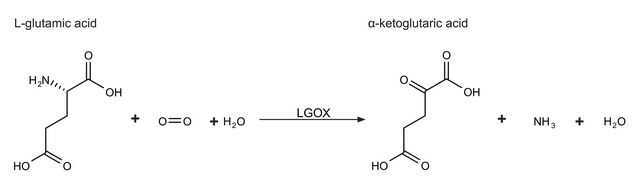
This enzyme is useful for enzymatic determination of NH3, α-ketoglutaric acid and L-glutamic acid, and for assay of leucine aminopeptidase and urease. This enzyme is also used for enzymatic determination of urea when coupled with urease (URH-201) in clinical analysis. In vitro, various activity assays of this enzyme examine the conversion of α-ketoglutarate to L-glutamate, in the presence of excess ammonium ions (NH4+) and NADPH.
Biochem/physiol Actions
L-glutamic dehydrogenase catalyzes the conversion of glutamate to α-ketoglutarate.
Physical properties
Isoelectric point : 4.6
Michaelis constants : 1.1 X 10-3M (NH3), 3.4 X 10-4M (α-Ketoglutarate)
1.2 X 10-3M (L-Glutamate), 1.4 X 10-5M (NADPH), 1.5 X 10-5M (NADP+)
Structure : 6 subunits (M.W.50,000) per mol of enzyme
Inhibitors : Hg++, Cd++, p-chloromercuribenzoate, pyridine, 4-4′-dithiopyridine,
2,2′-dithiopyridine
Optimum pH : 8.5 (α-KG→L-Glu) 9.8 (L-Glu→α-KG)
Optimum temperature : 45oC(α-KG−L-Glu) 45-55oC (L-Glu→α-KG)
pH stability : pH 6.0 - 8.5 (25oC, 20hr)
Thermal stability : below 50oC (pH 7.4, 10min)
Michaelis constants : 1.1 X 10-3M (NH3), 3.4 X 10-4M (α-Ketoglutarate)
1.2 X 10-3M (L-Glutamate), 1.4 X 10-5M (NADPH), 1.5 X 10-5M (NADP+)
Structure : 6 subunits (M.W.50,000) per mol of enzyme
Inhibitors : Hg++, Cd++, p-chloromercuribenzoate, pyridine, 4-4′-dithiopyridine,
2,2′-dithiopyridine
Optimum pH : 8.5 (α-KG→L-Glu) 9.8 (L-Glu→α-KG)
Optimum temperature : 45oC(α-KG−L-Glu) 45-55oC (L-Glu→α-KG)
pH stability : pH 6.0 - 8.5 (25oC, 20hr)
Thermal stability : below 50oC (pH 7.4, 10min)
Unit Definition
One unit will reduce 1.0 μmole of α-ketoglutarate to L-glutamate per min at pH 8.3 at 30 °C in the presence of ammonium ions and NADPH.
Physical form
Solution in 50 mM Tris HCl, pH 7.8, 5 mM Na2EDTA containing 0.05% sodium azide
Other Notes
Note: Do not confuse with non-specific L-GLDH, EC 1.4.1.3.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
J Bailey et al.
The Journal of biological chemistry, 257(10), 5579-5583 (1982-05-25)
The activity of bovine liver glutamate dehydrogenase is affected in several ways depending on substrate concentrations and pH. At ph 6.5 and below, both oxidative deamination and reductive amination reactions are inhibited by ADP. At pH 7.0 and above both
D P Hornby et al.
The Biochemical journal, 223(1), 161-168 (1984-10-01)
In steady-state kinetic studies of ox liver glutamate dehydrogenase in 0.11 M-potassium phosphate buffer, pH7, at 25 degrees C, the concentration of ADP was varied from 0.5 to 1000 microM. Inhibition was observed except when the concentrations of both glutamate
Daria V Borsakova et al.
Scientific reports, 12(1), 5437-5437 (2022-04-02)
Excessive ammonium blood concentration causes many serious neurological complications. The medications currently used are not very effective. To remove ammonium from the blood, erythrocyte-bioreactors containing enzymes that processing ammonium have been proposed. The most promising bioreactor contained co-encapsulated glutamate dehydrogenase
Tomomi Abiko et al.
Planta, 232(2), 299-311 (2010-05-06)
In plants, glutamine synthetase (GS) is the enzyme that is mainly responsible for the assimilation of ammonium. Conversely, in microorganisms such as bacteria and Ascomycota, NADP(H)-dependent glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH) and GS both have important roles in ammonium assimilation. Here, we
Daniel Juan Herrera et al.
Annals of clinical biochemistry, 47(Pt 1), 81-83 (2009-11-27)
Enzymatic assays using glutamate dehydrogenase (GLDH) to monitor the transformation of NAD(P)H to NAD(P)(+) by a spectrophotometric technique are the most common methods to measure plasma ammonia (PA) in routine laboratories worldwide. However, these assays can potentially be subject to
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service