G2133
Glucose Oxidase from Aspergillus niger
Type VII, lyophilized powder, ≥100,000 units/g solid (without added oxygen)
Synonym(s):
β-D-Glucose:oxygen 1-oxidoreductase, G.Od., GOx
About This Item
Recommended Products
type
Type VII
Quality Level
form
lyophilized powder
specific activity
≥100,000 units/g solid (without added oxygen)
mol wt
160 kDa
does not contain
extender
composition
Protein, ≥60%
application(s)
diagnostic assay manufacturing
foreign activity
Catalase ≤10 Sigma units/mg protein
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
−20°C
InChI
1S/C6H12O6/c7-1-2-3(8)4(9)5(10)6(11)12-2/h2-11H,1H2/t2-,3-,4+,5-,6-/m1/s1
InChI key
WQZGKKKJIJFFOK-VFUOTHLCSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
pI: 4.2
Extinction coefficient: E1% = 16.7 (280 nm)
Glucose oxidase from Aspergillus niger is a dimer consisting of 2 equal subunits with a molecular mass of 80 kDa each. Each subunit contains one flavin adenine dinulceotide moiety and one iron. The enzyme is a glycoprotein containing ~16% neutral sugar and 2% amino sugars. The enzyme also contains 3 cysteine residues and 8 potential sites for N-linked glycosylation.
Glucose oxidase is capable of oxidizing D-aldohexoses, monodeoxy-D-glucoses, and methyl-D-glucoses at varying rates.
The pH optimum for glucose oxidase is 5.5, while it has a broad activity range of pH 4-7. Glucose oxidase is specific for β-D-glucose with a KM of 33-110 mM.
Glucose oxidase does not require any activators, but it is inhibited by Ag+, Hg2+, Cu2+, phenylmercuric acetate, and p-chloromercuribenzoate. It is not inhibited by the nonmetallic SH reagents: N-ethylmaleimide, iodoacetate, and iodoacetamide.
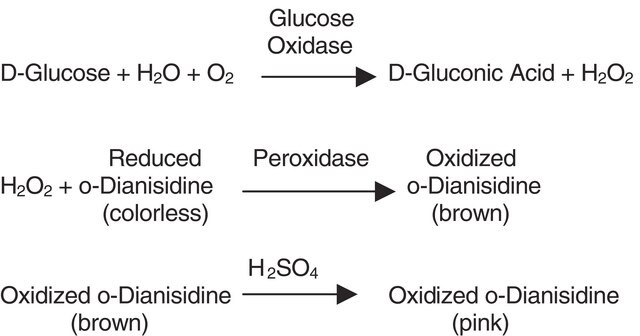
Glucose oxidase can be utilized in the enzymatic determination of D-glucose in solution. As glucose oxidase oxidizes β-D-glucose to D-gluconolactate and hydrogen peroxide, horseradish peroxidase is often used as the coupling enzyme for glucose determination. Although glucose oxidase is specific for β-D-glucose, solutions of D-glucose can be quantified as α-D-glucose will mutorotate to β-D-glucose as the β-D-glucose is consumed by the enzymatic reaction.
Application
a) Biosensor development:
- Diazoresin nanofilm coatings on alginate microspheres: Srivastava, R. et al., Biotechnol. Bioeng., 91(1), 124-131 (2005).
- Paper-based glucose biosensor: Lankelma, J. et al., Anal. Chem., 84(9), 417-4152 (2012)
- Microfluidic device with glucose oxidase immobilized on hydrogel for glucose analysis of blood: He, R.-Y. et al., RSC Adv., 9, 32367-32374 (2019).
c) Enzymatic fuel-cells with chitosan-based membranes: Bahar, T., and Yazici, M.S., Electroanalysis, 32(6), 1304-1314 (2020).
Biochem/physiol Actions
Quality
Unit Definition
Physical form
Analysis Note
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Personal Protective Equipment
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Protocols
To measure glucose oxidase activity, a continuous spectrophotometric rate-determination assay is used at 500 nm. One unit will oxidize 1 μmol of β-D-glucose to D-gluconolactone and hydrogen peroxide per minute.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service