C9301
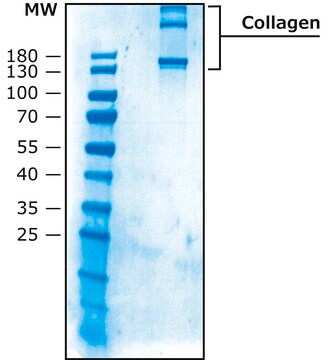
Chicken Collagen Type II
from chicken sternal cartilage, powder, suitable for cell culture
About This Item
Recommended Products
product name
Collagen from chicken sternal cartilage, Type II (Miller), powder, BioReagent, suitable for cell culture
biological source
chicken (Sternal cartilage)
Quality Level
type
Type II (Miller)
product line
BioReagent
form
powder
packaging
glass bottle of 100 mg
poly bottle of 25 mg
glass bottle of 5 mg
concentration
60-80% (biuret)
technique(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
surface coverage
6‑10 μg/cm2
solubility
acetic acid: 0.5-2.0 mg/mL (Dissolve for several hours at 2-8 °C, occasionally swirling.)
UniProt accession no.
Binding Specificity
Peptide Source: Fibrinogen
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
2-8°C
Gene Information
chicken ... COL2A1(395069)
Related Categories
General description
Application
- in enzyme–linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
- chondrocyte-mediated tissue production in vitro.
- induction, treatment and assessment of collagenα induced arthritis (CIA).
- cell proliferation assay.
- as a coating for cell culture surfaces.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Features and Benefits
Other Notes
Preparation Note
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Cancer stem cell media, spheroid plates and cancer stem cell markers to culture and characterize CSC populations.
Extracellular matrix proteins such as laminin, collagen, and fibronectin can be used as cell attachment substrates in cell culture.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service