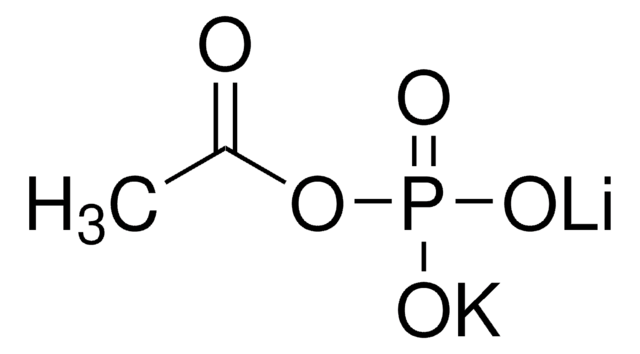
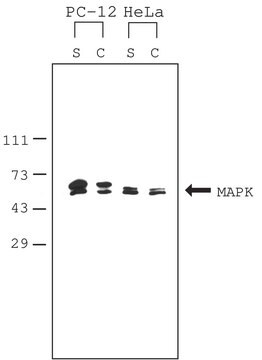
C4482
CelLytic™ Y Cell Lysis Reagent
For yeast cells
Synonym(s):
Yeast cell lysis reagent
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
form
solution
General description
Application
Features and Benefits
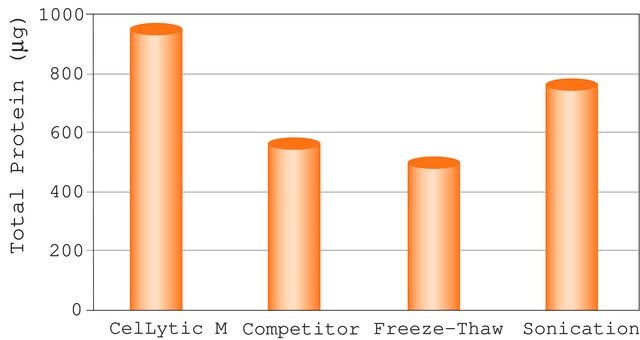
- Fast: Cell lysis in just 20 minutes
- Efficient: Three times more efficient than glass beads
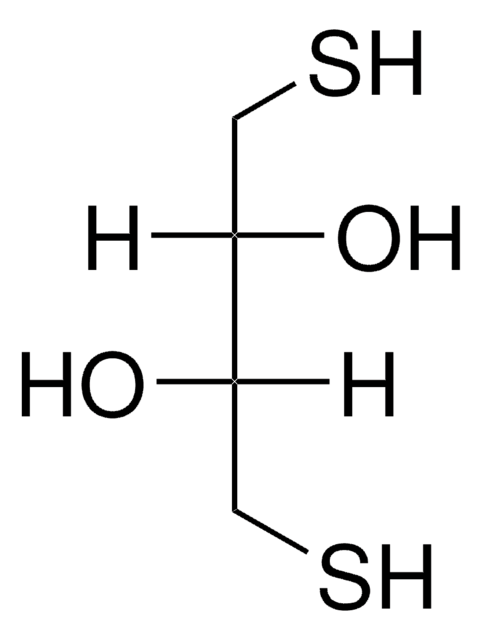
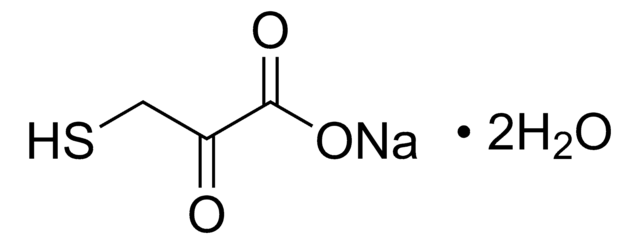
- Flexible: Lysis is enhanced by the addition of reducing reagent (DTT)
- Gentle: Non-denaturing - preserves biological activity
Legal Information
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Aquatic Chronic 3 - Eye Irrit. 2
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 3
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
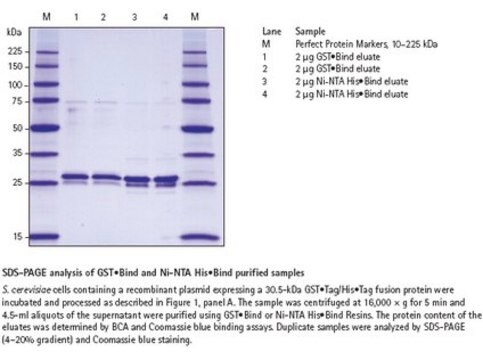
Our yeast cell lysis reagents are versatile, phosphate-free, and non-denaturing. CelLytic Y Cell Lysis reagent provides an effective method for yeast cell lysis and protein solubilization. The CelLytic Y Yeast Enzymatic Lysis Kit provides a convenient method for a highly efficient spheroplast formation and protein extraction from Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Pichia Pastoris and Schizosaccharomyces pombe yeast strains.
ReadyShield® phosphatase and protease inhibitor cocktail FAQ for sample protection in a variety of cell types and tissue extracts, including mammalian, plant, and microbial samples. Our ReadyShield® Protease Inhibitor Cocktail is a non-freezing solution that contains inhibitors with a broad specificity for serine, cysteine, acid proteases and aminopeptidases.
Related Content
An overview of cell lysis and protein extraction methods including detergent solubilization, freeze-thaw lysis, osmotic shock, sonication, enzymatic cell lysis, and mechanical disruption techniques such as Dounce, Polytron, and mortar and pestle homogenization.
An overview of cell lysis and protein extraction methods including detergent solubilization, freeze-thaw lysis, osmotic shock, sonication, enzymatic cell lysis, and mechanical disruption techniques such as Dounce, Polytron, and mortar and pestle homogenization.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service