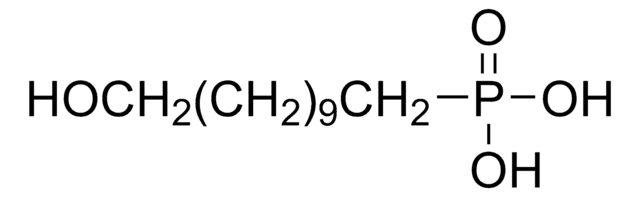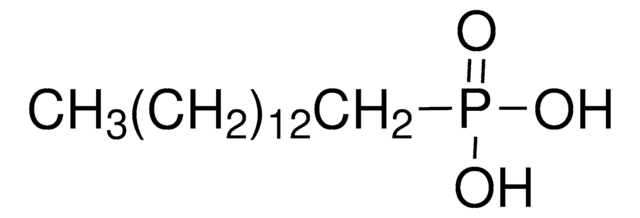736244
Hexadecylphosphonic acid
97%
Synonym(s):
n-Hexadecylphosphonic acid, HDPA
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
Assay
97%
form
solid
mp
88-93 °C
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
CCCCCCCCCCCCCCCCP(O)(O)=O
InChI
1S/C16H35O3P/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14-15-16-20(17,18)19/h2-16H2,1H3,(H2,17,18,19)
InChI key
JDPSFRXPDJVJMV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Related Categories
General description
Application
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
There is widespread demand for thin, lightweight, and flexible electronic devices such as displays, sensors, actuators, and radio-frequency identification tags (RFIDs). Flexibility is necessary for scalability, portability, and mechanical robustness.
Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) have attracted enormous interest for a wide variety of applications in micro- and nano-technology. In this article, we compare the benefits of three different classes of SAM systems (alkylthiolates on gold).
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service