H6030
Anti-HSV antibody produced in rabbit
affinity isolated antibody, buffered aqueous solution
Synonym(s):
Anti-Herpes Simplex Virus
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
rabbit
Quality Level
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
affinity isolated antibody
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
polyclonal
form
buffered aqueous solution
technique(s)
immunoprecipitation (IP): 1.0 μg/mL
western blot: 2.5 μg/mL
storage temp.
−20°C
target post-translational modification
unmodified
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
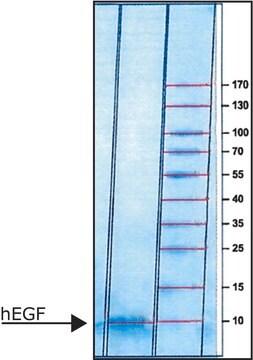
Recognizes N- and C-terminal HSV fusion proteins.
Immunogen
synthetic peptide corresponding to amino acids 290−300 of glycoprotein-D precursor, an envelop component of herpes simplex virus.
Application
Anti-HSV antibody was used to expand the repertoire of plasmids for PCR-mediated epitope tagging in yeast.
Applications in which this antibody has been used successfully, and the associated peer-reviewed papers, are given below.
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (1 paper)
Western Blotting (1 paper)
Chromatin immunoprecipitation (1 paper)
Western Blotting (1 paper)
Biochem/physiol Actions
Anti-HSV is developed in rabbits using a synthetic peptide (K-QPELAPEDPED) conjugated to KLH via the N-terminal lysine. The peptide corresponds to amino acids 290-300 of Glycoprotein D precursor which is an envelope component of herpes simplex virus. Anti-HSV antibody reacts specifically with HSV tagged fusion proteins, using immunoblotting and immunoprecipitation techniques.
Physical form
Solution in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4, containing 1% bovine serum albumin and 15 mM sodium azide.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
WGK
nwg
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Expanding the repertoire of plasmids for PCR-mediated epitope tagging in yeast
Moqtaderi Z, Struhl K
Yeast, 4, 287-292 (2008)
Obstetrical roundabout.
H E Cudby
Midwives chronicle, 91(1089), 301-301 (1978-10-01)
P O Olins et al.
Current opinion in biotechnology, 4(5), 520-525 (1993-10-01)
Recent advances in protein expression in E. coli have focused primarily on the enhancement of protein quality. Problems in mRNA translation such as inefficient initiation, mistranslation, frame-shifting and frame-hopping can often be addressed by altering heterologous gene-coding sequences. Fusion technology
Christine E Cucinotta et al.
PLoS genetics, 11(8), e1005420-e1005420 (2015-08-05)
Eukaryotes regulate gene expression and other nuclear processes through the posttranslational modification of histones. In S. cerevisiae, the mono-ubiquitylation of histone H2B on lysine 123 (H2B K123ub) affects nucleosome stability, broadly influences gene expression and other DNA-templated processes, and is
Zarmik Moqtaderi et al.
Yeast (Chichester, England), 25(4), 287-292 (2008-03-14)
Epitope tagging of yeast proteins provides a convenient means of tracking proteins of interest in Western blots and immunoprecipitation experiments without the need to raise and test specific antibodies. We have constructed four plasmids for use as templates in PCR-based
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service