C8649
Cholesterol Oxidase from Streptomyces sp.
lyophilized powder, ≥20 units/mg protein
Synonym(s):
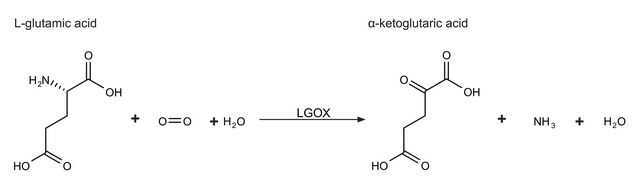
Cholesterol: oxygen oxidoreductase
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
Streptomyces sp.
form
lyophilized powder
specific activity
≥20 units/mg protein
mol wt
~34 kDa
composition
protein, 55-65% biuret
solubility
50 mM potassium phosphate buffer, pH 7.0: soluble (Cold)
shipped in
dry ice
storage temp.
−20°C
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
Biochem/physiol Actions
Physical properties
Michaelis constant : 4.3 x 10‾5M(Cholesterol)
Inhibitors : Ionic detergents, Hg++, Ag+
Optimum pH : 6.5 − 7.0
Optimum temperature : 45 – 50°C
pH Stability : pH 5.0 – 10.0 (25°C, 20hr)
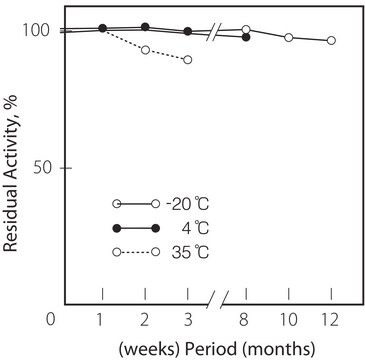
Thermal stability : Below 45°C (pH 7.0, 15min)
Unit Definition
Physical form
Preparation Note
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Protocols
Protocol for Assay Procedure for Cholesterol Oxidase
This procedure applies to products that have a specification for the enzymatic activity of cholesterol oxidase. This assay is NOT to be used to assay Cholesterol Oxidase from Schizophyllum commune (Discontinued Product Number C7274) and from Brevibacterium sp. (Discontinued Product Number C8153).
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service