CT02
MTT Cell Growth Assay Kit
MTT Cell Growth Assay is a colorimetric assay that can be used for either proliferation or complement-mediated cytotoxicity assays.
Synonym(s):
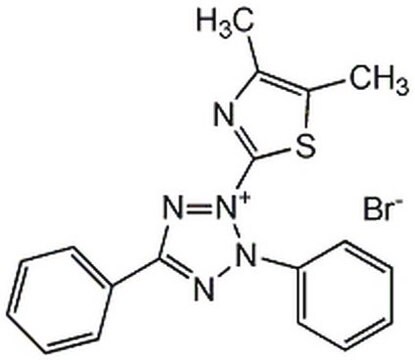
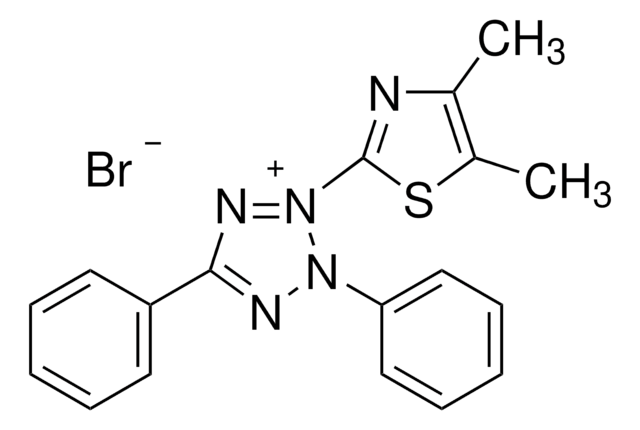
Formazan-based mitochondria cytotoxicity assay
About This Item
Recommended Products
Quality Level
manufacturer/tradename
Chemicon®
technique(s)
activity assay: suitable
cell based assay: suitable
shipped in
wet ice
General description
Application
1) Carry out a lymphokine, mitogen, or complement-mediated cytotoxicity assay using standard methods, in 96-well flat-bottomed tissue culture plates of good optical quality (e.g. Falcon). The final volume of tissue culture medium in each well should be 0.1 mL, and the medium (e.g. RPMI or DMEM) may contain up to 10% Fetal Bovine Serum.
2) At the end of the assay add 0.01 mL AB Solution (MTT) to each well. Mix by tapping gently on the side of the tray.
3) Incubate at 37° C for cleavage of MTT to occur. Optimal times may vary according to the assay, but four hours is suitable for most purposes. At the end of this time, the MTT formazan produced in wells containing live cells will appear as black, fuzzy crystals on the bottom of the well.
4) Add 0.1 mL isopropanol with 0.04 N HCl to each well. Mix thoroughly by repeated pipetting with a multichannel pipettor. The HCl converts the phenol red in tissue culture medium to a yellow color that does not interfere with MTT formazan measurement. The isopropanol dissolves the formazan to give a homogeneous blue solution suitable for absorbance measurement.
5) Within an hour, measure the absorbance on an ELISA plate reader with a test wavelength of 570 nm and a reference wavelength of 630 nm. After several hours at room temperature, serum proteins may begin to precipitate due to the acid/alcohol. Chilling the plates will hasten the precipitation. If the plates must be stored before measuring, keep at 4° C before adding the acid/alcohol, then warm to room temperature and add acid/alcohol just before reading.
Results:
The MTT assay will normally detect 200 to 50,000 cells of a typical cell line, although 1,000 to 50,000 is the useful range. This number may vary for other cell types. Cytotoxic assays should be set up so that the control, unlysed cells give a signal of 0.2 to 0.4, and proliferation assays should yield a similar value at plateau concentrations. This corresponds to about 20-50,000 cells per well with a typical cell line.
Absorbance is directly proportional to the number of cells; actual cells do not absorb significantly, even up to concentrations of 1 x 106 cells/mL.
Components
Solution B: PBS pH 7.4, 15 mL
Storage and Stability
Reagent Preparation:
Add 10 mL Solution B to one vial of Reagent A. Mix well, sterile filter and keep in the dark at 4° C until used. Note: It may take overnight to dissolve. Do not heat solution. When absolutely required to dissolve crystals, adjust pH with 1-2 drops of HCl. The AB mixture is stable for several weeks under these conditions.
Legal Information
Disclaimer
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Muta. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Cell based assays for cell proliferation (BrdU, MTT, WST1), cell viability and cytotoxicity experiments for applications in cancer, neuroscience and stem cell research.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service