T1567
Tertiapin-Q trifluoroacetate salt
≥97% (HPLC)
Sinónimos:
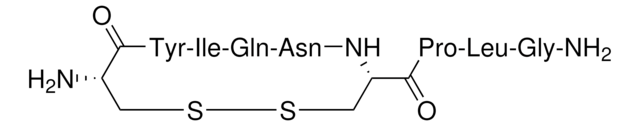
[Gln13]-Tertiapin, Ala-Leu-Cys-Asn-Cys-Asn-Arg-Ile-Ile-Ile-Pro-His-Gln-Cys-Trp-Lys-Lys-Cys-Gly-Lys-Lys-NH2 [Disulfide bridges 3–14, 5–18], TPNQ
Iniciar sesiónpara Ver la Fijación de precios por contrato y de la organización
About This Item
Fórmula empírica (notación de Hill):
C106H175N35O24S4
Número de CAS:
Peso molecular:
2452.00
Número MDL:
Código UNSPSC:
12352200
NACRES:
NA.32
Productos recomendados
Nivel de calidad
Ensayo
≥97% (HPLC)
Formulario
lyophilized
temp. de almacenamiento
−20°C
Información sobre el gen
human ... KCNJ1(3758)
mouse ... KCNJ1(56379)
rat ... KCNJ1(24521)
Amino Acid Sequence
Ala-Leu-Cys-Asn-Cys-Asn-Arg-Ile-Ile-Ile-Pro-His-Gln-Cys-Trp-Lys-Lys-Cys-Gly-Lys-Lys-NH2 [Disulfide bridges 3–14, 5–18]
Acciones bioquímicas o fisiológicas
Blocks the GIRK1/4 and ROMK1 members of the inward-rectifier K+ channel family.
Otras notas
Non-air oxidizable tertiapin derivative.
Lyophilized from 0.1% TFA in H2O
Código de clase de almacenamiento
11 - Combustible Solids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Equipo de protección personal
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Synthesis of a stable form of tertiapin: a high-affinity inhibitor for inward-rectifier K+ channels.
W Jin et al.
Biochemistry, 38(43), 14286-14293 (1999-11-26)
Tertiapin (TPN), a small protein derived from honey bee venom, inhibits the GIRK1/4 and ROMK1 channels with nanomolar affinities. Methionine residue 13 in TPN interacts with residue F148 in the channel, located just outside of the narrow region of the
W Jin et al.
Biochemistry, 38(43), 14294-14301 (1999-11-26)
Tertiapin-Q (TPN(Q)) is a derivative of honey bee toxin tertiapin (TPN) whose methionine residue is replaced with a glutamine residue. TPN(Q) inhibits the ROMK1 and GIRK1/4 inward-rectifier K(+) channels with affinities very similar to TPN. However, unlike native TPN, TPN(Q)
W Jin et al.
Biochemistry, 37(38), 13291-13299 (1998-09-28)
Inward-rectifier K+ channels are a group of highly specialized K+ channels that accomplish a variety of important biological tasks. Inward-rectifier K+ channels differ from voltage-activated K+ channels not only functionally but also structurally. Each of the four subunits of the
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico