SRP0119
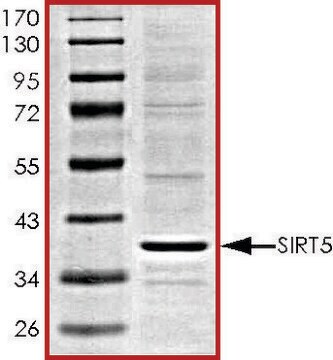
Sirtuin 5 human
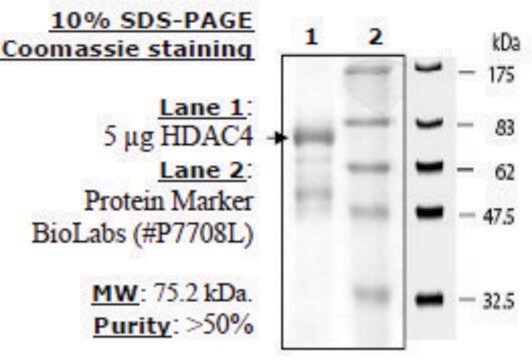
recombinant, expressed in E. coli, ≥50% (SDS-PAGE)
Sinónimos:
NAD-dependent ADP-ribosyltransferase sirtuin-5, SIR2L5, SIRT5, sir2-like 5
About This Item
Productos recomendados
origen biológico
human
recombinante
expressed in E. coli
Análisis
≥50% (SDS-PAGE)
formulario
aqueous solution
mol peso
59.8 kDa
envase
pkg of 100 μg
condiciones de almacenamiento
avoid repeated freeze/thaw cycles
concentración
>0.02 mg/mL
Nº de acceso NCBI
Nº de acceso UniProt
Condiciones de envío
dry ice
temp. de almacenamiento
−70°C
Información sobre el gen
human ... SIRT5(23408)
Descripción general
Human Sirtuin 5, GenBank Accession No. NM_012241), full length with N-terminal ST tag, MW = 59.8kDa, expressed in Escherichia coli expression system.
Aplicación
Acciones bioquímicas o fisiológicas
Forma física
Nota de preparación
Código de clase de almacenamiento
10 - Combustible liquids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico