SML1661
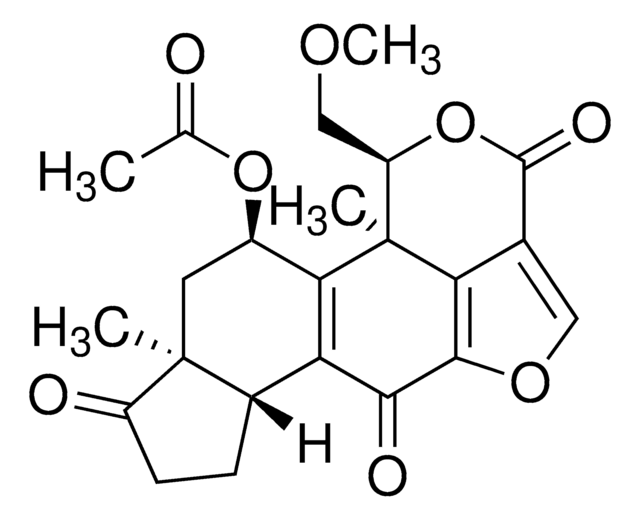
Bafilomycin A1
from Streptomyces griseus, ≥90% (HPLC), DMSO solution, V-ATPase inhibitor
Sinónimos:
BafA1
About This Item
Productos recomendados
product name
Bafilomycin A1 Ready Made Solution, 0.16 mM in DMSO, from Streptomyces griseus
origen biológico
Streptomyces griseus
Nivel de calidad
formulario
DMSO solution
concentración
0.16 mM in DMSO
Condiciones de envío
dry ice
temp. de almacenamiento
−20°C
InChI
1S/C35H58O9/c1-19(2)32-24(7)27(36)18-35(40,44-32)26(9)31(38)25(8)33-28(41-10)14-12-13-20(3)15-22(5)30(37)23(6)16-21(4)17-29(42-11)34(39)43-33/h12-14,16-17,19,22-28,30-33,36-38,40H,15,18H2,1-11H3/b14-12+,20-13+,21-16+,29-17-/t22-,23+,24-,25-,26-,27+,28-,30-,31+,32+,33+,35+/m0/s1
Clave InChI
XDHNQDDQEHDUTM-JQWOJBOSSA-N
Descripción general
Aplicación
- as an endosome acidification inhibitor to study the importance of endosome acidification in the extracellular vesicle uptake and cytosolic release of stably expressing NanoLuc luciferase-tagged Hsp70 (NLuc-Hsp70) in HeLa cells
- as a vacuolar-type H+-ATPase (V-ATPase) inhibitor to study its effects on autophagic turnover of light chain 3 β (LC3-II) in mice
- as an autophagy inhibitor to study its effects on primary rat liver sinusoidal endothelial cells (LSECs) defenestration
Acciones bioquímicas o fisiológicas
Otras notas
Código de clase de almacenamiento
10 - Combustible liquids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 1
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
188.6 °F - closed cup
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
87 °C - closed cup
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico