SML1620
NGI-1
≥95% (HPLC)
Sinónimos:
5-[(Dimethylamino)sulfonyl]-N-(5-methyl-2-thiazolyl)-2-(1-pyrrolidinyl)-benzamide, ML414
Iniciar sesiónpara Ver la Fijación de precios por contrato y de la organización
About This Item
Fórmula empírica (notación de Hill):
C17H22N4O3S2
Número de CAS:
Peso molecular:
394.51
Código UNSPSC:
12352200
NACRES:
NA.77
Productos recomendados
Nivel de calidad
Ensayo
≥95% (HPLC)
Formulario
powder
color
white to beige
solubilidad
DMSO: 5 mg/mL, clear (warmed)
temp. de almacenamiento
2-8°C
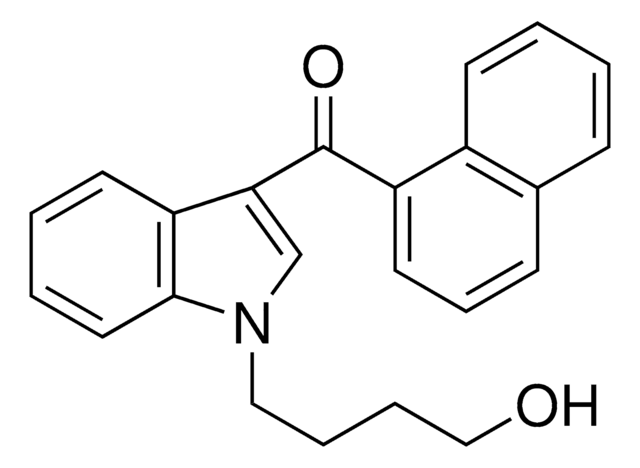
cadena SMILES
[S](=O)(=O)(N(C)C)c1cc(c(cc1)N3CCCC3)C(=O)Nc2[s]c(cn2)C
Acciones bioquímicas o fisiológicas
NGI-1 (ML414) is an inhibitor of Asparagine (N)-linked glycoslysation. NGI-1 inhibits the oligosaccharyltransferase, preventing the attachment to the protein. NGI-1 has been shown to induce senescence in receptor tyrosine kinase dependent tumors.
Código de clase de almacenamiento
11 - Combustible Solids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 3
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Lot/Batch Number
¿No ve la versión correcta?
Si necesita una versión concreta, puede buscar un certificado específico por el número de lote.
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Angelyn Larkin et al.
Biochemistry, 50(21), 4411-4426 (2011-04-22)
Asparagine-linked glycosylation involves the sequential assembly of an oligosaccharide onto a polyisoprenyl donor, followed by the en bloc transfer of the glycan to particular asparagine residues within acceptor proteins. These N-linked glycans play a critical role in a wide variety
Danielle Skropeta
Bioorganic & medicinal chemistry, 17(7), 2645-2653 (2009-03-17)
In a series of investigations, N-glycosylation has proven to be a key determinant of enzyme secretion, activity, binding affinity and substrate specificity, enabling a protein to fine-tune its activity. In the majority of cases elimination of all putative N-glycosylation sites
Cecilia Lopez-Sambrooks et al.
Nature chemical biology, 12(12), 1023-1030 (2016-10-25)
Asparagine (N)-linked glycosylation is a protein modification critical for glycoprotein folding, stability, and cellular localization. To identify small molecules that inhibit new targets in this biosynthetic pathway, we initiated a cell-based high-throughput screen and lead-compound-optimization campaign that delivered a cell-permeable
Ryan A Flynn et al.
Cell, 184(12), 3109-3124 (2021-05-19)
Glycans modify lipids and proteins to mediate inter- and intramolecular interactions across all domains of life. RNA is not thought to be a major target of glycosylation. Here, we challenge this view with evidence that mammals use RNA as a
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico