SAB1403776
Monoclonal Anti-EP300 antibody produced in mouse
clone 1D2, ascites fluid
About This Item
Productos recomendados
origen biológico
mouse
conjugado
unconjugated
forma del anticuerpo
ascites fluid
tipo de anticuerpo
primary antibodies
clon
1D2, monoclonal
mol peso
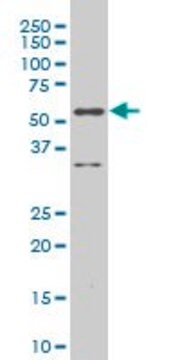
antigen ~37.11 kDa
reactividad de especies
human
técnicas
indirect ELISA: suitable
western blot: 1:500-1:1000
isotipo
IgG1
Nº de acceso NCBI
Nº de acceso UniProt
Condiciones de envío
dry ice
temp. de almacenamiento
−20°C
modificación del objetivo postraduccional
unmodified
Información sobre el gen
human ... EP300(2033)
Categorías relacionadas
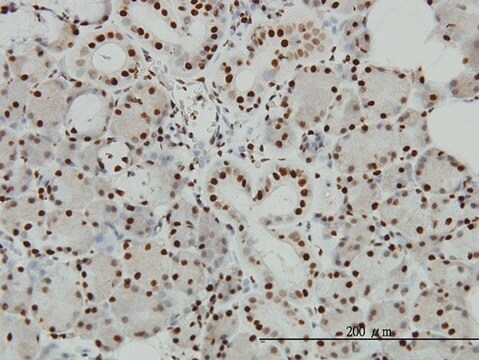
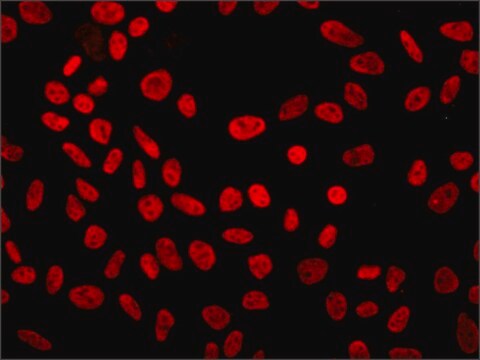
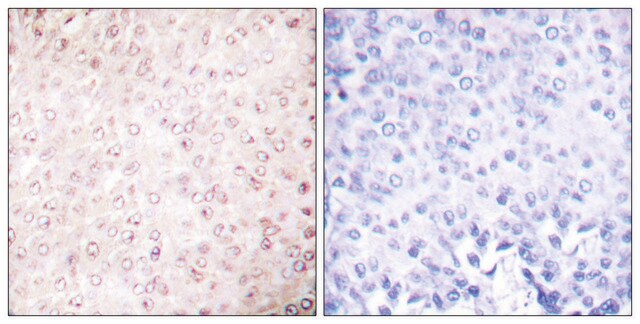
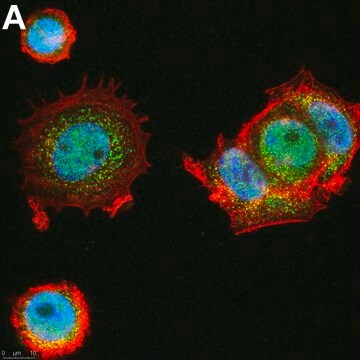
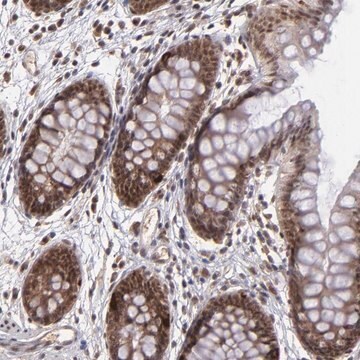
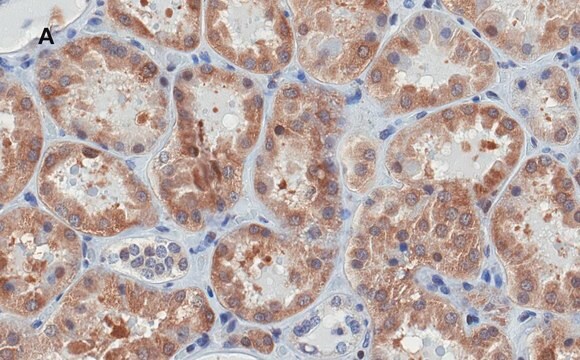
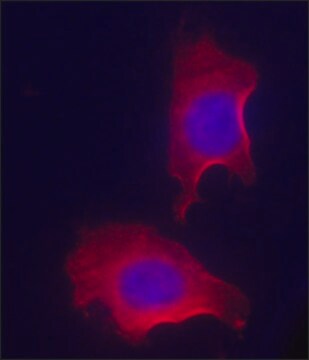
Descripción general
Inmunógeno
Sequence
PPLQHHGQLAQPGALNPPMGYGPRMQQPSNQGQFLPQTQFPSQGMNVTNIPLAPSSGQAPVSQAQMSSSSCPVNSPIMPPGSQGSHIHCPQLPQPALHQN
Acciones bioquímicas o fisiológicas
Forma física
¿No encuentra el producto adecuado?
Pruebe nuestro Herramienta de selección de productos.
Opcional
Código de clase de almacenamiento
11 - Combustible Solids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 1
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico