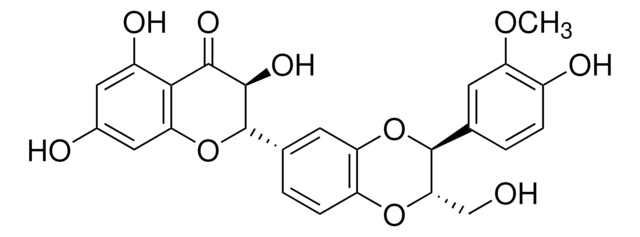
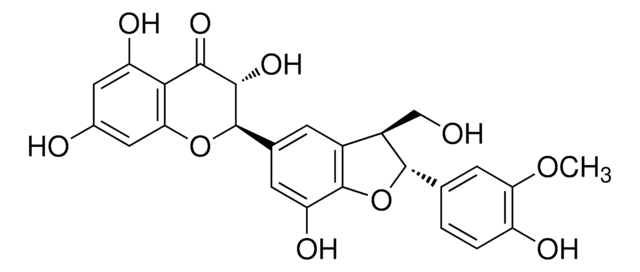
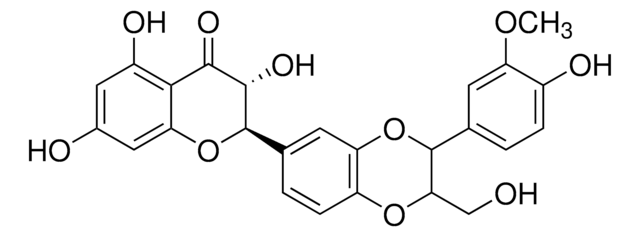
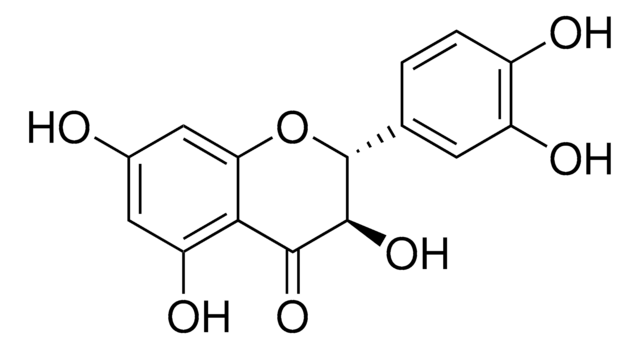
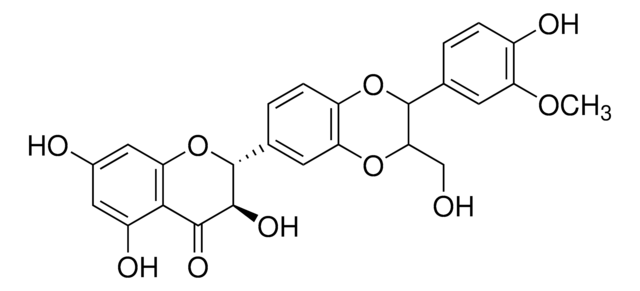
S0292
Silymarin
flavonolignans
Sinónimos:
flavolignans
About This Item
Productos recomendados
origen biológico
plant (Silybum marianum)
Nivel de calidad
Formulario
powder
técnicas
toxicology assay: suitable
aplicaciones
microbiology
temp. de almacenamiento
−20°C
InChI
1S/C25H22O10/c1-32-17-6-11(2-4-14(17)28)24-20(10-26)33-16-5-3-12(7-18(16)34-24)25-23(31)22(30)21-15(29)8-13(27)9-19(21)35-25/h2-9,20,23-29,31H,10H2,1H3
Clave InChI
SEBFKMXJBCUCAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Descripción general
Aplicación
- its in vitro antiviral, antibacterial, antifungal activities and cytotoxicity
- its effect of silymarin on bladder contractions in cyclophosphamide (CYP)-induced cystitis rat model
- its effect on liver toxication induced by Fumonisin B1 in mice
Acciones bioquímicas o fisiológicas
Otras notas
Código de clase de almacenamiento
11 - Combustible Solids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Equipo de protección personal
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Artículos
Antioxidants protect biological systems from oxidative damage produced by oxygen-containing free radicals and from redoxactive transition metal ions such as iron, copper, and cadmium.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico