P6374
p53 human
recombinant, expressed in baculovirus infected Sf21 cells
About This Item
Productos recomendados
origen biológico
human
Nivel de calidad
recombinante
expressed in baculovirus infected Sf21 cells
Ensayo
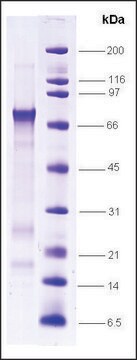
≥90% (SDS-PAGE)
Formulario
aqueous solution
técnicas
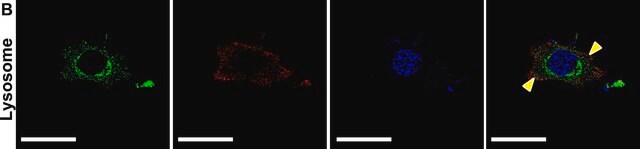
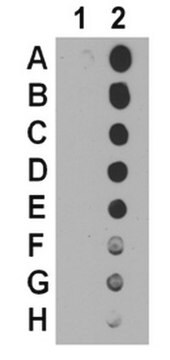
dot blot: suitable
Nº de acceso UniProt
aplicaciones
genomic analysis
Condiciones de envío
dry ice
temp. de almacenamiento
−70°C
Información sobre el gen
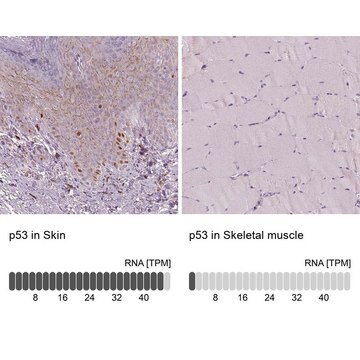
human ... TP53(7157)
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
Descripción general
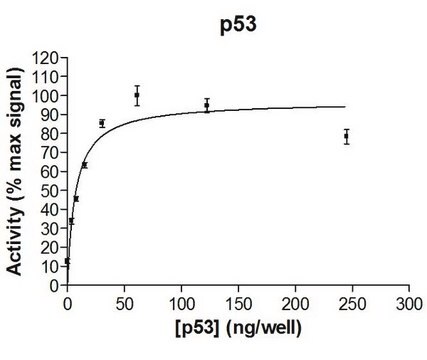
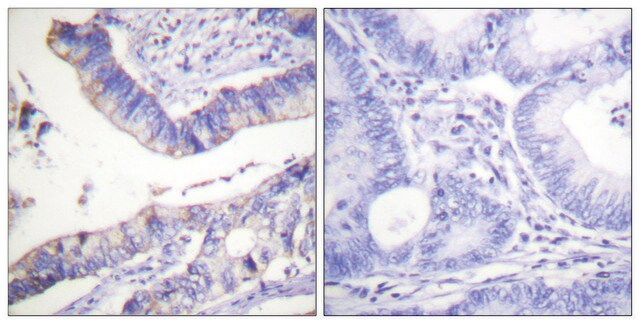
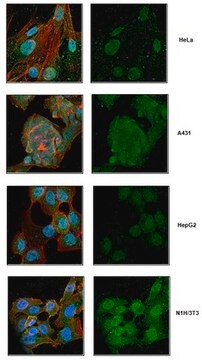
Aplicación
Acciones bioquímicas o fisiológicas
Propiedades físicas
Forma física
Código de clase de almacenamiento
10 - Combustible liquids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Artículos
Huntington's disease (HD) is an autosomal dominant, late-onset neurodegenerative disorder characterized by a selective neuronal cell death in the cortex and striatum leading to cognitive dysfunction, motor impairment and behavioral changes.
We present an article about how proliferating cells require the biosynthesis of structural components for biomass production and for genomic replication.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico