MSP12
Membrane Scaffold Protein 2N2
recombinant, expressed in E. coli, MSP1D1-MSP1D2 fusion protein
Sinónimos:
Membrane scaffold protein
Iniciar sesiónpara Ver la Fijación de precios por contrato y de la organización
About This Item
Código UNSPSC:
12352200
NACRES:
NA.26
Productos recomendados
recombinante
expressed in E. coli
Nivel de calidad
Análisis
≥90% (SDS-GE)
formulario
buffered aqueous solution
mol peso
45,541.2 Da
solubilidad
water: soluble
Condiciones de envío
ambient
temp. de almacenamiento
−20°C
Descripción general
Research area: Cell Struc
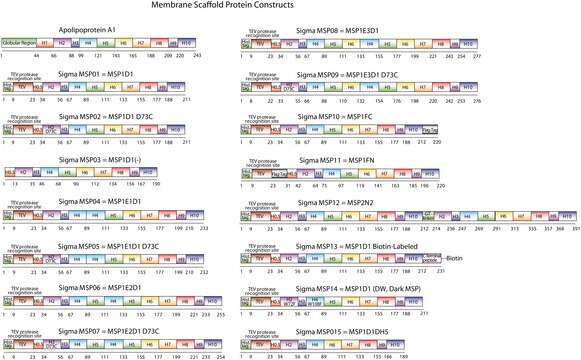
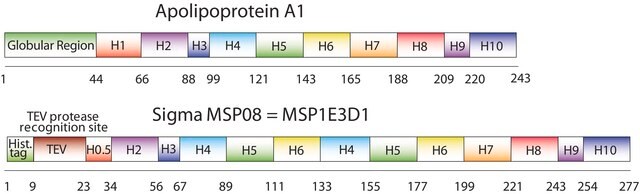
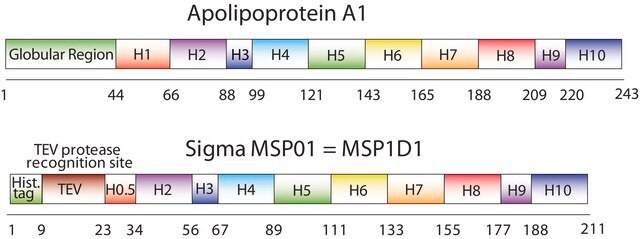
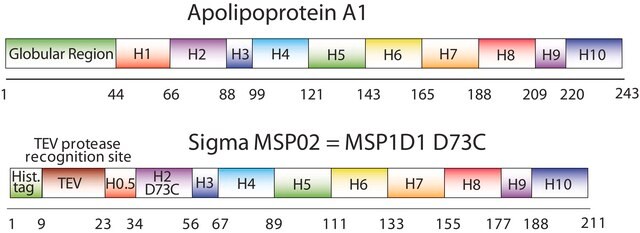
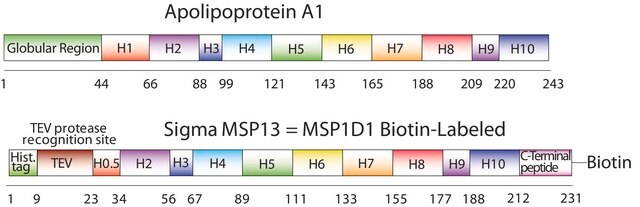
The first MSP, MSP1, was engineered with its sequence based on the sequence of A-1 but without the globular N-terminal domain of native A-1. The Membrane Scaffold Protein 1D1 (MSP1D1) variant of MSP1 deletes the first 11 amino acids in the Helix 1 portion (referred to as “H0.5” in the accompanying figure) of the original MSP1 sequence. Membrane Scaffold Protein 2N2 (MSP 2N2) is a fusion of MSP1D1 and another MSP variant, MSP1D2. MSP1D2 deletes the first 22 amino acids of the original MSP sequence (i.e. the entire H1 segment). In MSP2N2, a GT linker connects MSP1D1 and MSP1D2.
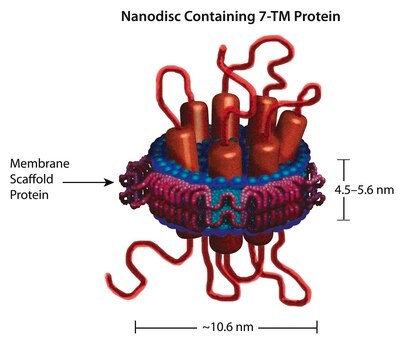
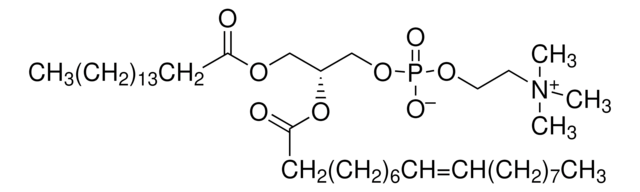
Nanodisc technology is an approach rendering membrane proteins soluble in aqueous solutions in a native-like bilayer environment, where the membrane proteins remain stable and active. The Nanodisc concept is derived from high-density lipoprotein (HDL) particles and their primary protein component, apolipoprotein. The Nanodisc is a non-covalent structure of phospholipid bilayer and membrane scaffold protein (MSP), a genetically engineered protein that mimics the function of Apolipoprotein A-1 (ApoA-1).
The first MSP, MSP1, was engineered with its sequence based on the sequence of A-1 but without the globular N-terminal domain of native A-1. The Membrane Scaffold Protein 1D1 (MSP1D1) variant of MSP1 deletes the first 11 amino acids in the Helix 1 portion (referred to as “H0.5” in the accompanying figure) of the original MSP1 sequence. Membrane Scaffold Protein 2N2 (MSP 2N2) is a fusion of MSP1D1 and another MSP variant, MSP1D2. MSP1D2 deletes the first 22 amino acids of the original MSP sequence (i.e. the entire H1 segment). In MSP2N2, a GT linker connects MSP1D1 and MSP1D2.
Nanodisc technology is an approach rendering membrane proteins soluble in aqueous solutions in a native-like bilayer environment, where the membrane proteins remain stable and active. The Nanodisc concept is derived from high-density lipoprotein (HDL) particles and their primary protein component, apolipoprotein. The Nanodisc is a non-covalent structure of phospholipid bilayer and membrane scaffold protein (MSP), a genetically engineered protein that mimics the function of Apolipoprotein A-1 (ApoA-1).
Aplicación
Membrane Scaffold Protein 2N2 has been used in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) and for reconstitution of human β3 homopentameric gamma-aminobutyric acid type A receptor (GABAAR) in nanodiscs.
Acciones bioquímicas o fisiológicas
Scaffold proteins play a crucial role in providing specificity to the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway, which is essential for normal cellular functions and development. They help regulate the localization of MAPK components, allowing for targeted modulation of cellular responses without affecting global MAPK activity.
Información legal
Nanodisc technology, and many of its uses, are covered by the following patents held by the University of Illinois.
- 7,691,414 Membrane scaffold proteins
- 7,662,410 Membrane scaffold proteins and embedded membrane proteins
- 7,622,437 Tissue factor compositions and methods
- 7,592,008 Membrane scaffold proteins
- 7,575,763 Membrane scaffold proteins and tethered membrane proteins
- 7,083,958 Membrane scaffold proteins
- 7,048,949 Membrane scaffold proteins
Código de clase de almacenamiento
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 2
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Tomasz Uchański et al.
Nature methods, 18(1), 60-68 (2021-01-08)
Nanobodies are popular and versatile tools for structural biology. They have a compact single immunoglobulin domain organization, bind target proteins with high affinities while reducing their conformational heterogeneity and stabilize multi-protein complexes. Here we demonstrate that engineered nanobodies can also
Protocolos
Protocols for Membrane Scaffold Proteins and Nanodisc Formation
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico