MBD0013
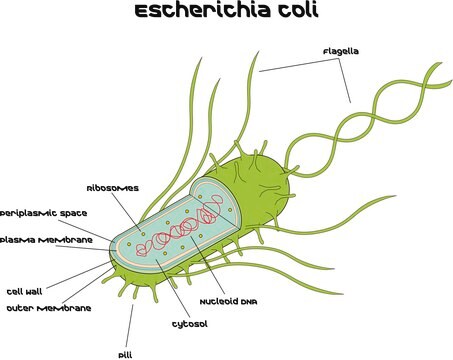
Microbial DNA standard from Escherichia coli
Suitable for PCR, sequencing and NGS, 10 ng/μL
Sinónimos:
E.Coli
About This Item
Productos recomendados
Nivel de calidad
formulario
liquid
concentración
10 ng/μL
técnicas
DNA extraction: suitable
DNA sequencing: suitable
PCR: suitable
idoneidad
suitable for restriction endonuclease digests, PCR amplification, Southern blots, and sequencing reactions
Condiciones de envío
ambient
temp. de almacenamiento
−20°C
Descripción general
Read here how to use our standards to ensure data integrity for your microbiome research.
Aplicación
Suitable for Quantitative standard for PCR, Sequencing and NGS
Características y beneficios
- Individual microbial standard for microbiomics and meta-genomics workflow
- Suitable standard for PCR, sequencing and NGS
- Improve Bioinformatics analyses
- Increases reproducibility
- Compare results lab to lab
Forma física
Otras notas
Código de clase de almacenamiento
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 1
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Artículos
An overview of human microbiome research, workflow challenges, sequencing, library production, data analysis, and available microbiome reagents to support your research.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico