G5545
Anti-β-Glucuronidase (C-Terminal) antibody produced in rabbit
~1.5 mg/mL, affinity isolated antibody, buffered aqueous solution
Sinónimos:
Anti-GUS
Iniciar sesiónpara Ver la Fijación de precios por contrato y de la organización
About This Item
conjugado:
unconjugated
application:
WB
clon:
polyclonal
reactividad de especies:
plant
citations:
5
técnicas:
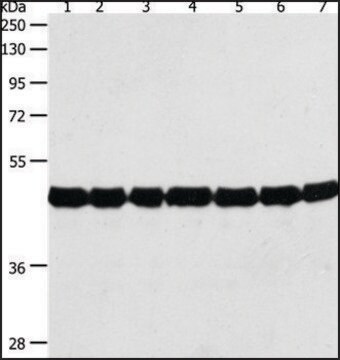
western blot: 1-2 μg/mL using purified GUS from E. coli
Productos recomendados
origen biológico
rabbit
Nivel de calidad
conjugado
unconjugated
forma del anticuerpo
affinity isolated antibody
tipo de anticuerpo
primary antibodies
clon
polyclonal
Formulario
buffered aqueous solution
mol peso
antigen 60 kDa
reactividad de especies
plant
concentración
~1.5 mg/mL
técnicas
western blot: 1-2 μg/mL using purified GUS from E. coli
Condiciones de envío
dry ice
temp. de almacenamiento
−20°C
modificación del objetivo postraduccional
unmodified
Descripción general
β-Glucuronidase (GUS) gene (also referred to as uidA) from Escherichia- coli, codes for a 60kDa protein.
Especificidad
Anit-β-Glucuronidase (C-Terminal) recognizes bacterial GUS expressed in transgenic tobacco plants.
The antibody recognizes bacterial GUS expressed in transgenic tobacco plants.
Inmunógeno
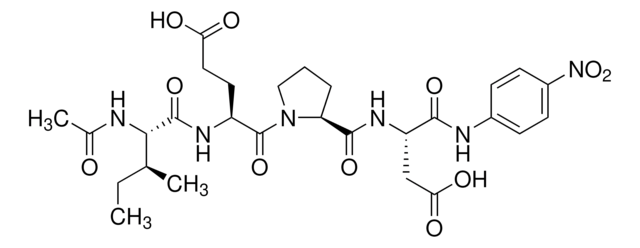
synthetic peptide corresponding to amino acids 589-603 at the C-terminus of E. coli GUS, conjugated to KLH.
Aplicación
Detection of GUS by immunoblotting (60 kDa). Staining of the GUS band in immunoblotting is specifically inhibited by the immunizing GUS peptide (E. coli, amino acids 589-603).
Acciones bioquímicas o fisiológicas
β-Glucuronidase (GUS) acts as a reporter gene for plant studies. Reporter genes are widely used for studying the expression of foreign genes in transformed plant tissues. GUS is an hydrolase that catalyzes the cleavage of a variety of β-glucuronide derivatives available for colorimetric, fluorometric and histochemical assays. GUS activity is easily assayed in vitro and can withstand fixation, enabling histochemical localization in cells and tissue sections. However, one of the major limitations of the gus reporter gene system is that the histochemical GUS assay system is destructive for the plant tissue, and therefore it is not suitable for direct visual selection of transformed plants.
Forma física
Solution in 0.01 M phosphate buffered saline, pH 7.4, containing 15 mM sodium azide.
Nota de preparación
The antibody is affinity-purified using the immunizing peptide immobilized on agarose.
Cláusula de descargo de responsabilidad
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
¿No encuentra el producto adecuado?
Pruebe nuestro Herramienta de selección de productos.
Producto relacionado
Referencia del producto
Descripción
Precios
Código de clase de almacenamiento
10 - Combustible liquids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Benjamin Dugdale et al.
The Plant cell, 25(7), 2429-2443 (2013-07-11)
In this study, we describe a novel protein production platform that provides both activation and amplification of transgene expression in planta. The In Plant Activation (INPACT) system is based on the replication machinery of tobacco yellow dwarf mastrevirus (TYDV) and
Mark D Harrison et al.
Plant biotechnology journal, 9(8), 884-896 (2011-03-02)
A major strategic goal in making ethanol from lignocellulosic biomass a cost-competitive liquid transport fuel is to reduce the cost of production of cellulolytic enzymes that hydrolyse lignocellulosic substrates to fermentable sugars. Current production systems for these enzymes, namely microbes
Sebastian N W Hoernstein et al.
Molecular & cellular proteomics : MCP, 15(6), 1808-1822 (2016-04-14)
Protein arginylation is a posttranslational modification of both N-terminal amino acids of proteins and sidechain carboxylates and can be crucial for viability and physiology in higher eukaryotes. The lack of arginylation causes severe developmental defects in moss, affects the low
Biolistic-mediated genetic transformation of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) and stable Mendelian inheritance of transgenes
Ivo Nayche L, et al.
Plant Cell Reports, 27(9), 1475-1483 (2008)
Transgenic Plants: Gene Constructs, Vector and Transformation Method
New Visions in Plant Science (2018)
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico