C4963
Catalase−polyethylene glycol
lyophilized powder, ~40,000 units/mg protein
Sinónimos:
PEG-Catalase
Iniciar sesiónpara Ver la Fijación de precios por contrato y de la organización
About This Item
Productos recomendados
Formulario
lyophilized powder
Nivel de calidad
actividad específica
~40,000 units/mg protein
mol peso
PEG 5,000
composición
Protein, ~50% E405
Extensión del etiquetado
~40 mol PEG per mol protein
unión a la matriz
secondary amine linkage.
temp. de almacenamiento
−20°C
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
Aplicación
Pulmonary artery endothelial cells treated with PEG-catalase showed effective inhibition of 20- HETE (hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid)-induced increase in fluorescence. However, the experiment excludes potential nonspecific fluorescence of DCF (dichlorofluorescein). This experiment studied the effect of 20-HETE on superoxide production and NADPH oxidase activation.
Acciones bioquímicas o fisiológicas
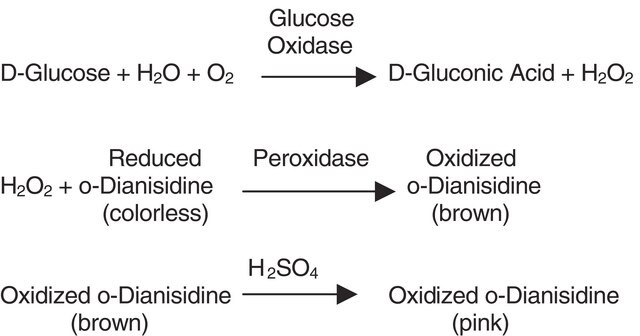
Catalase from bovine liver catalyzes the decomposition of H2O2 into water and oxygen. It is a tetramer consisting of four equal subunits with a molecular weight of 60 kDa each. Each subunit contains iron bound to a protoheme IX group. The enzyme also strongly binds NADP, which is in close proximity to the heme group. Catalase activity is constant over the pH range of 4.0-8.5. The pI is found to be 5.4. The enzyme activity is inhibited by 3-amino-1-H-1,2,4 triazole, cyanide, azide, hydroxylamine, cyanogen bromide, 2-mercaptoethanol, dithiothreitol, dianisidine, and nitrate. Incubation of catalase with ascorbate or ascorbate/Cu2+ results in degradation of the catalase molecule. It does not require any activators.
Envase
Package size based on protein content
Otras notas
Catalase from bovine liver coupled to methoxy-polyethylene glycol.
Forma física
Contains PEG plus 5% citrate buffer salts
Código de clase de almacenamiento
11 - Combustible Solids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Equipo de protección personal
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Joe Nassour et al.
Nature communications, 7, 10399-10399 (2016-01-30)
The main characteristic of senescence is its stability which relies on the persistence of DNA damage. We show that unlike fibroblasts, senescent epithelial cells do not activate an ATM-or ATR-dependent DNA damage response (DDR), but accumulate oxidative-stress-induced DNA single-strand breaks
Jeremiah D Keyes et al.
Free radical biology & medicine, 112, 534-543 (2017-08-28)
ERK-dependent signaling is key to many pathways through which extracellular signals are transduced into cell-fate decisions. One conundrum is the way in which disparate signals induce specific responses through a common, ERK-dependent kinase cascade. While studies have revealed intricate ways
Emeric Deruy et al.
PloS one, 5(9), e12712-e12712 (2010-09-22)
Senescence is a state of growth arrest resulting mainly from telomere attrition and oxidative stress. It ultimately leads to cell death. We have previously shown that, in keratinocytes, senescence is induced by NF-kappaB activation, MnSOD upregulation and H(2)O(2) overproduction. We
Kathleen D Metzler et al.
Cell reports, 8(3), 883-896 (2014-07-30)
Neutrophils contain granules loaded with antimicrobial proteins and are regarded as impermeable organelles that deliver cargo via membrane fusion. However, during the formation of neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs), neutrophil elastase (NE) translocates from the granules to the nucleus via an
Puvi N Seshiah et al.
Circulation research, 91(5), 406-413 (2002-09-07)
Angiotensin II (Ang II)-stimulated hypertrophy of vascular smooth muscle cells is mediated by reactive oxygen species (ROS) derived from NAD(P)H oxidases. The upstream signaling mechanisms by which Ang II activates these oxidases are unclear but may include protein kinase C
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico