C0871
Anti-Cullin 3 antibody produced in rabbit
~1.0 mg/mL, affinity isolated antibody, buffered aqueous solution
Sinónimos:
Anti-CUL3
About This Item
Productos recomendados
origen biológico
rabbit
Nivel de calidad
conjugado
unconjugated
forma del anticuerpo
affinity isolated antibody
tipo de anticuerpo
primary antibodies
clon
polyclonal
Formulario
buffered aqueous solution
mol peso
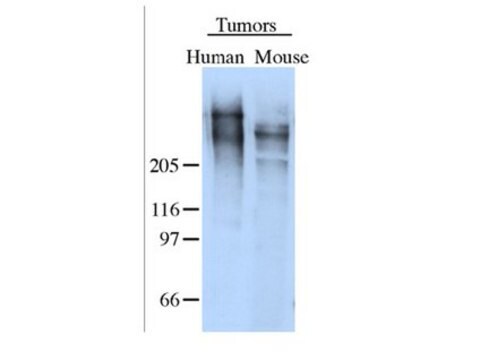
antigen ~80 kDa
reactividad de especies
rat, mouse, human
concentración
~1.0 mg/mL
técnicas
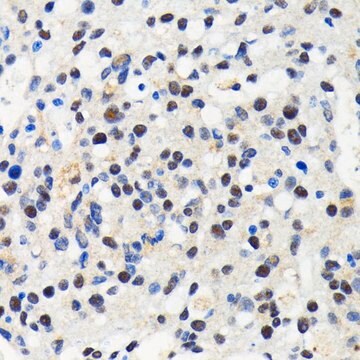
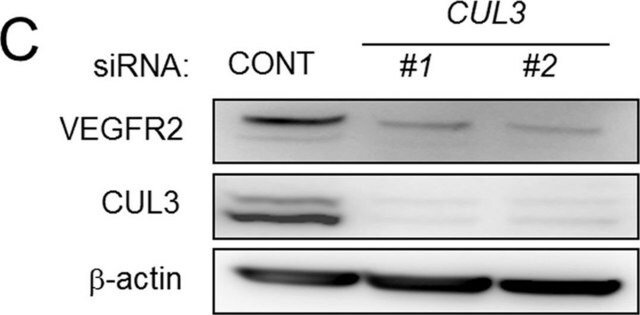
immunoprecipitation (IP): 5-10 μg using lysate of rat brain
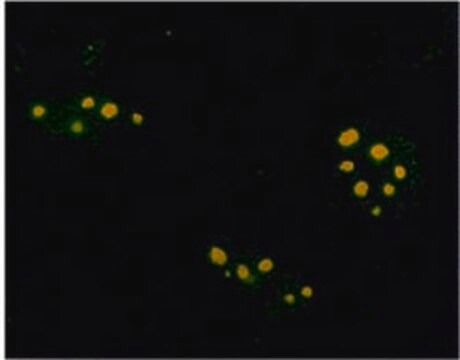
indirect immunofluorescence: 5-10 μg/mL using mouse 3T3 cells
western blot: 1-2 μg/mL using whole extract of HEK-293T cells expressing human Cullin 3
Nº de acceso UniProt
Condiciones de envío
dry ice
temp. de almacenamiento
−20°C
modificación del objetivo postraduccional
unmodified
Información sobre el gen
human ... CUL3(8452)
mouse ... Cul3(26554)
rat ... Cul3(301555)
Descripción general
Aplicación
- western blotting
- immunoprecipitation
- immunofluorescence
Acciones bioquímicas o fisiológicas
Forma física
Cláusula de descargo de responsabilidad
¿No encuentra el producto adecuado?
Pruebe nuestro Herramienta de selección de productos.
Producto relacionado
Código de clase de almacenamiento
10 - Combustible liquids
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Equipo de protección personal
Eyeshields, Gloves, multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US)
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
Certificados de análisis (COA)
¿No ve la versión correcta?
Si necesita una versión concreta, puede buscar un certificado específico por el número de lote.
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico