B6688
BMS 493
≥98% (HPLC), powder, pan-RAR inverse agonist
Sinónimos:
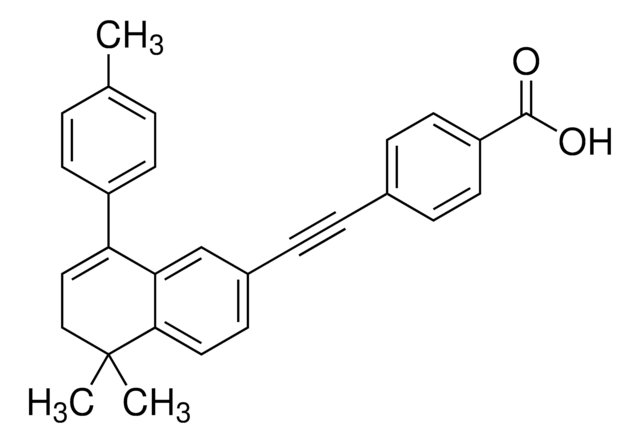
(E)-4-[2-[5,6-Dihydro-5,5-dimethyl-8-(2-phenylethynyl)naphthalen-2-yl]ethen-1-yl]benzoic acid, 4-[(1E)-2-[5,6-Dihydro-5,5-dimethyl-8-(phenylethynyl)-2-naphthalenyl]ethenyl]-benzoic acid, BMS204, 493
About This Item
Productos recomendados
product name
BMS 493, ≥98% (HPLC)
Análisis
≥98% (HPLC)
formulario
powder
color
light yellow to yellow
solubilidad
DMSO: ≥20 mg/mL
emisor
Bristol-Myers Squibb
temp. de almacenamiento
2-8°C
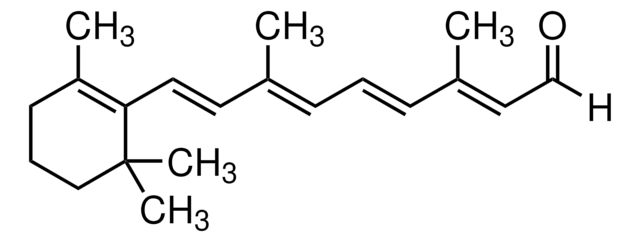
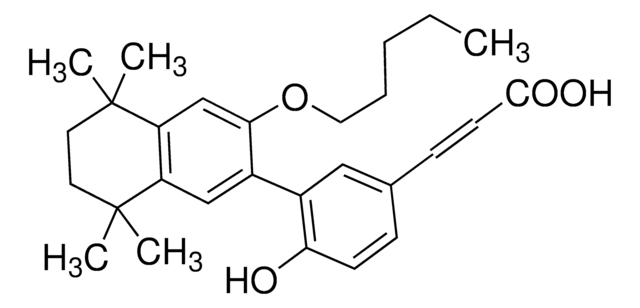
cadena SMILES
CC1(C)CC=C(C#Cc2ccccc2)c3cc(\C=C\c4ccc(cc4)C(O)=O)ccc13
InChI
1S/C29H24O2/c1-29(2)19-18-24(14-10-21-6-4-3-5-7-21)26-20-23(13-17-27(26)29)9-8-22-11-15-25(16-12-22)28(30)31/h3-9,11-13,15-18,20H,19H2,1-2H3,(H,30,31)/b9-8+
Clave InChI
YCADIXLLWMXYKW-CMDGGOBGSA-N
Descripción general
Aplicación
- as an inhibitor for the dietary and pharmacologic manipulation of retinoic acid (RA) activity in vivo and in vitro
- for human induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) culture and ventricular cardiomyocytes (VCMs) differentiation
- to inhibit retinoic acid (RA) signaling in explants
- as a retinoic acid receptor (RAR) inhibitor for the induction of synaptonemal complex protein 3 (SCP3) and ATP-dependent RNA helicase (DDX4) in primordial germ cells (PGCs)
Acciones bioquímicas o fisiológicas
Características y beneficios
Código de clase de almacenamiento
11 - Combustible Solids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 2
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Artículos
We offer many products related to non-steroid nuclear receptors for your research needs.
Contenido relacionado
Apoptosis, or programmed cell death (PCD), is a selective process for the removal of unnecessary, infected or transformed cells in various biological systems. As it plays a role in the homeostasis of multicellular organisms, apoptosis is tightly regulated through two principal pathways by a number of regulatory and effector molecules.
n proliferating cells, the cell cycle consists of four phases. Gap 1 (G1) is the interval between mitosis and DNA replication that is characterized by cell growth. Replication of DNA occurs during the synthesis (S) phase, which is followed by a second gap phase (G2) during which growth and preparation for cell division occurs. Together, these three stages comprise the interphase phase of the cell cycle. Interphase is followed by the mitotic (M) phase.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico