380R-2
Arginase-1 (EP261) Rabbit Monoclonal Primary Antibody
About This Item
Productos recomendados
origen biológico
rabbit
Nivel de calidad
100
500
conjugado
unconjugated
forma del anticuerpo
culture supernatant
tipo de anticuerpo
primary antibodies
clon
EP261, monoclonal
descripción
For In Vitro Diagnostic Use in Select Regions
formulario
buffered aqueous solution
reactividad de especies
human
envase
vial of 0.1 mL concentrate (380R-24)
vial of 0.1 mL concentrate Research Use Only (380R-24-RUO)
vial of 0.5 mL concentrate (380R-25)
vial of 1.0 mL concentrate (380R-26)
vial of 1.0 mL concentrate Research Use Only (380R-26-RUO)
vial of 1.0 mL pre-dilute Research Use Only (380R-27-RUO)
vial of 1.0 mL pre-dilute ready-to-use (380R-27)
vial of 7.0 mL pre-dilute ready-to-use (380R-28)
vial of 7.0 mL pre-dilute ready-to-use Research Use Only (380R-28-RUO)
fabricante / nombre comercial
Cell Marque™
técnicas
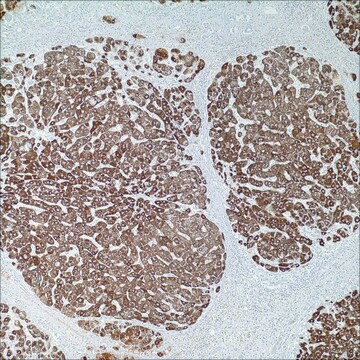
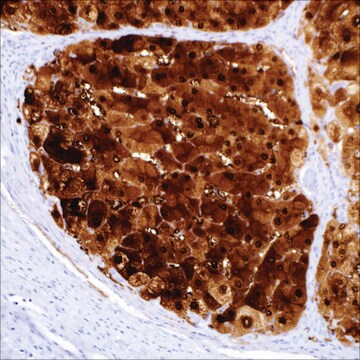
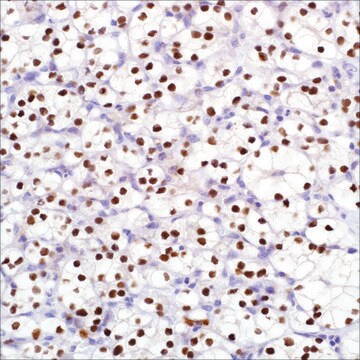
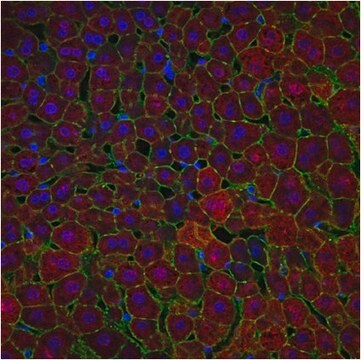
immunohistochemistry (formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections): 1:50-1:200 (concentrated)
isotipo
IgG
control
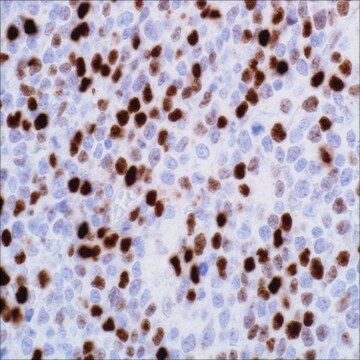
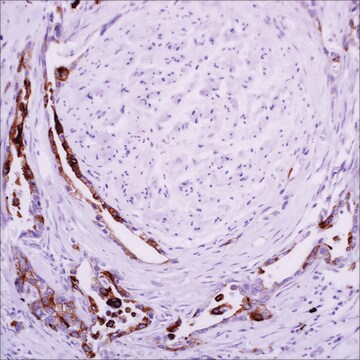
hepatocellular carcinoma, normal liver
Condiciones de envío
wet ice
temp. de almacenamiento
2-8°C
visualización
cytoplasmic, nuclear
Información sobre el gen
human ... ARG1(383)
Descripción general
Calidad
 IVD |  IVD |  IVD |  RUO |
Ligadura / enlace
Forma física
Nota de preparación
Note: This requires a keycode which can be found on your packaging or product label.
Download the latest released IFU
Note: This IFU may not apply to your specific product lot.
Otras notas
Información legal
¿No encuentra el producto adecuado?
Pruebe nuestro Herramienta de selección de productos.
Código de clase de almacenamiento
12 - Non Combustible Liquids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 2
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico