SCC284
EpH4 Mouse Mammary Epithelial Cell Line
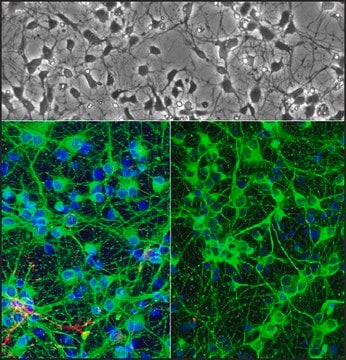
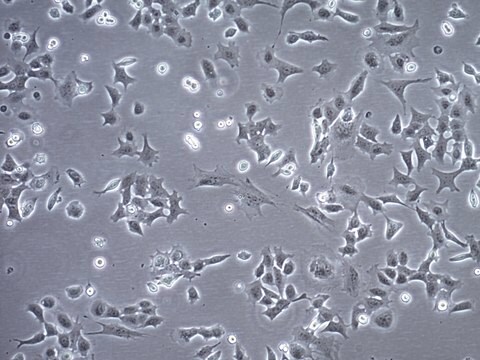
EpH4 mouse mammary epithelial cell line is a versatile system for studying a spectrum of morphological transformation spanning breast cancer metastasis, EMT, and hormonal regulation.
Iniciar sesiónpara Ver la Fijación de precios por contrato y de la organización
About This Item
Código UNSPSC:
41106514
NACRES:
NA.81
Productos recomendados
aplicaciones
cell analysis
Descripción general
Mammary epithelial cells are a model for cellular plasticity, the ability to undergo varied morphological changes. One of the significant aspects of mammary-derived tumors is epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT), which gives rise to the migratory behavior required for metastasis (1). Cellular plasticity makes mammary epithelial cell models valuable for the study of breast cancer malignancy in addition to hormonal regulation of differentiation and epithelial cell polarization.
Eph4 is a spontaneously immortalized cell line derived from primary murine mammary epithelial cells (2). EpH4 cells can be induced to synthesize milk proteins, such as caseins, upon the induction with lactogenic hormones such as prolactin, hydrocortisone, and insulin. For normal maintenance Eph4 cells should be cultured at high density (semi-confluency) and passaged before reaching confluency to avoid polarization and selective culture of single cells. Post-confluent Eph4 cells undergo polarization and formation of hemicysts or dome-like structures characterized by unidirectional transport of ions (3).
<bold>Source:</bold>
Eph4 cell line is a spontaneously immortalized clone derived from primary mammary epithelial cells of a female BALB/c mouse.
Research Category:
Cancer
Eph4 is a spontaneously immortalized cell line derived from primary murine mammary epithelial cells (2). EpH4 cells can be induced to synthesize milk proteins, such as caseins, upon the induction with lactogenic hormones such as prolactin, hydrocortisone, and insulin. For normal maintenance Eph4 cells should be cultured at high density (semi-confluency) and passaged before reaching confluency to avoid polarization and selective culture of single cells. Post-confluent Eph4 cells undergo polarization and formation of hemicysts or dome-like structures characterized by unidirectional transport of ions (3).
<bold>Source:</bold>
Eph4 cell line is a spontaneously immortalized clone derived from primary mammary epithelial cells of a female BALB/c mouse.
Research Category:
Cancer
Origen línea celular
Mouse, Epithelial Cells
Envase
≥1X106 cells/vial
Almacenamiento y estabilidad
Store in liquid nitrogen. The cells can be cultured for at least 10 passages after initial thawing without significantly affecting the cell marker expression and functionality.
Otras notas
This product is intended for sale and sold solely to academic institutions for internal academic research use per the terms of the “Academic Use Agreement” as detailed in the product documentation. For information regarding any other use, please contact licensing@emdmillipore.com.
Cláusula de descargo de responsabilidad
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Código de clase de almacenamiento
10 - Combustible liquids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 1
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico