NA61
Anti-BrdU (Ab-3) Mouse mAb (Mobu-1)
liquid, clone Mobu-1, Calbiochem®
Sinónimos:
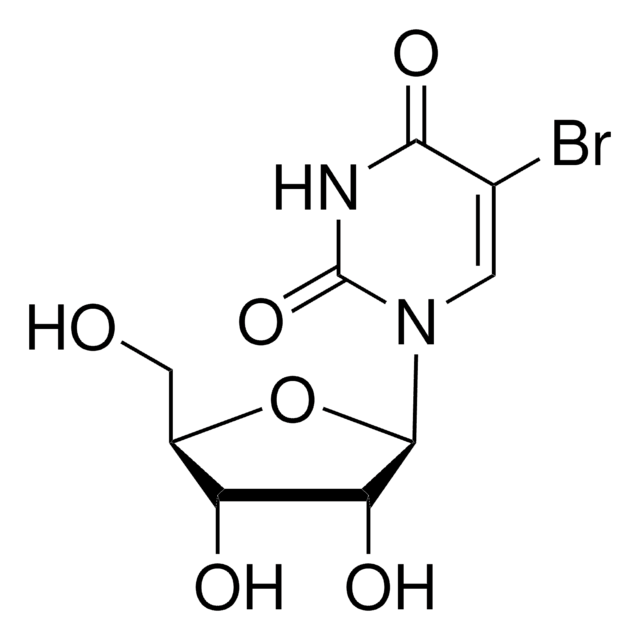
Anti-Bromodeoxyuridine
About This Item
Productos recomendados
origen biológico
mouse
Nivel de calidad
forma del anticuerpo
purified antibody
tipo de anticuerpo
primary antibodies
clon
Mobu-1, monoclonal
formulario
liquid
contiene
≤0.1% sodium azide as preservative
reactividad de especies (predicha por homología)
all
fabricante / nombre comercial
Calbiochem®
condiciones de almacenamiento
do not freeze
isotipo
IgG1
Condiciones de envío
wet ice
temp. de almacenamiento
2-8°C
modificación del objetivo postraduccional
unmodified
Descripción general
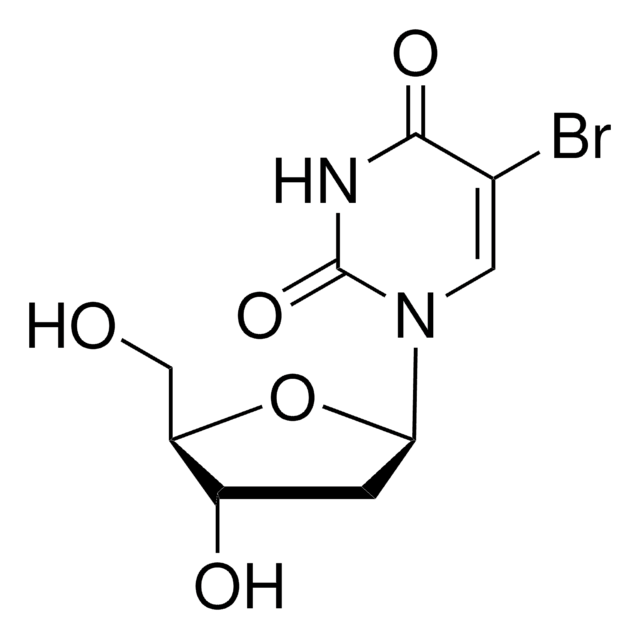
Inmunógeno
Aplicación
Frozen Sections (2 g/ml)
Immunocytochemistry (1 g/ml)
Paraffin Sections (2.5 g/ml, trysin pre-treatment required)
Immunoblotting (not recommended)
Envase
Advertencia
Forma física
Nota de análisis
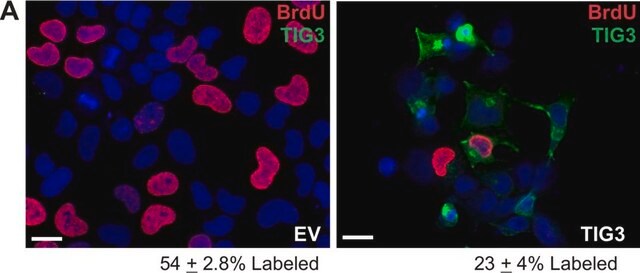
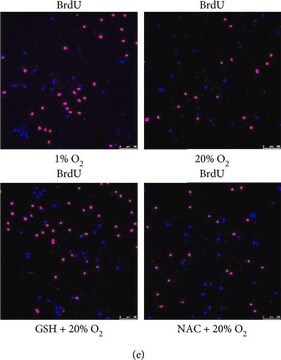
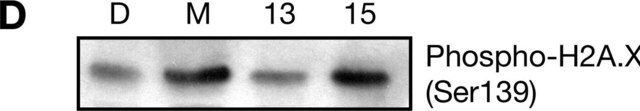
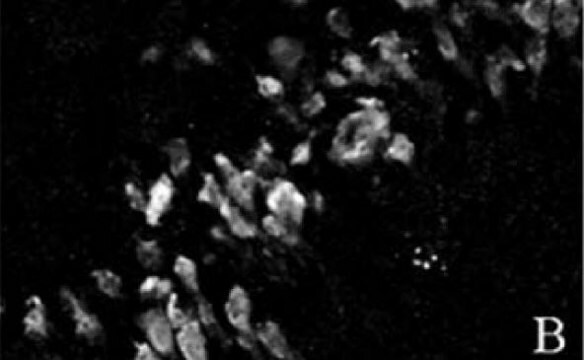
Unlabeled cells
BrdU labeled DNA
Otras notas
Gratzner, H.G. and Leif, R.C. 1981. Cytometry1, 385.
Gratzner, H.G. et al. 1975. Exp. Cell Res.95, 88.
Información legal
¿No encuentra el producto adecuado?
Pruebe nuestro Herramienta de selección de productos.
Código de clase de almacenamiento
11 - Combustible Solids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 1
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico