MAB1618
Anti-Dynein Antibody, 74 kDa Intermediate chains, cytoplasmic, clone 74.1
clone 74.1, Chemicon®, from mouse
Sinónimos:
Cytoplasmic dynein 1 intermediate chain 1, Cytoplasmic dynein intermediate chain 1, Dynein intermediate chain 1, cytosolic, DH IC-1, Cytoplasmic dynein 1 intermediate chain 2, Cytoplasmic dynein intermediate chain 2, Dynein intermediate chain 2, cytosoli
About This Item
Productos recomendados
origen biológico
mouse
Nivel de calidad
forma del anticuerpo
purified antibody
tipo de anticuerpo
primary antibodies
clon
74.1, monoclonal
reactividad de especies
Xenopus, mouse, fish, rat, human, sheep, Drosophila, bovine
no debe reaccionar con
squid
fabricante / nombre comercial
Chemicon®
técnicas
immunocytochemistry: suitable
immunofluorescence: suitable
immunoprecipitation (IP): suitable
western blot: suitable
isotipo
IgG2b
Nº de acceso NCBI
Condiciones de envío
wet ice
modificación del objetivo postraduccional
unmodified
Información sobre el gen
human ... DYNC1I1(1780)
Descripción general
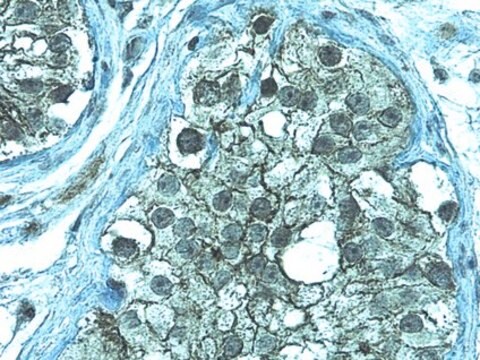
Especificidad
Aplicación
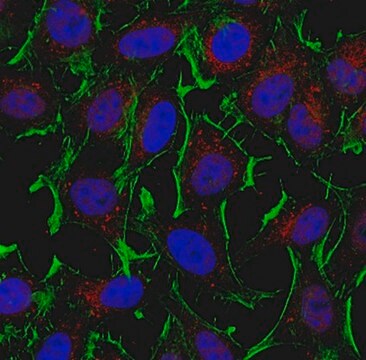
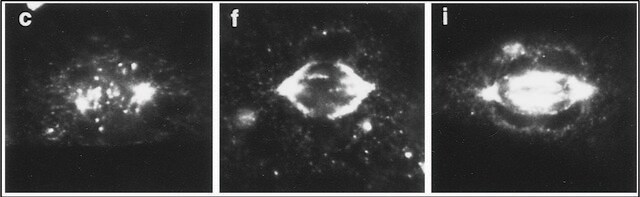
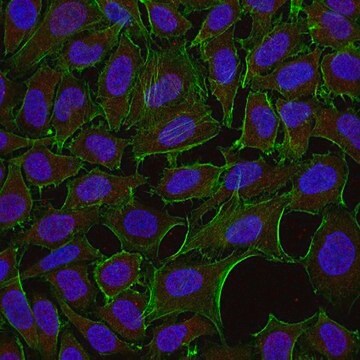
1:50-1:100 dilution from a previous lot was used. Reacts with cultured MDCK cells, NRR cells, N1E cells, and PTK-1 cells.
Immunoprecipitation:
10 μL of a previous lot per 0.5 gm tissue was used. The monoclonal cleanly immunoprecipitates the entire dynein complex stoichiometrically from TX-100 or NP-40 lysates (including the 530 kD heavy chain, the light intermediate chains and the light chains) from various tissues and cultured cell lines. If detergents such as SDS are used to prepare the lysates the only dynein subunits which are immunoprecipitated are the IC74 subunits (presumably because the dynein complex dissociates), and other contaminating proteins can be found in SDS immunoprecipitates.
Immunoblotting:
1:1,000-1:5000. Reacts with cultured MDCK cells, PC-12 cells, N1E cells, neurons, glia and other cultured cells.
Optimal working dilutions must be determined by end user.
Calidad
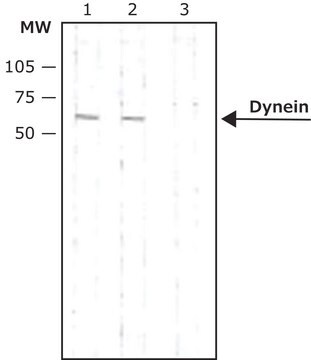
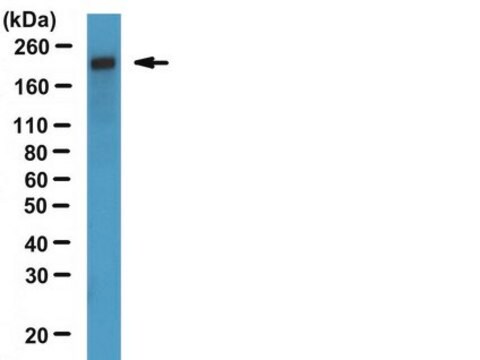
Western Blot Analysis:
1:500 dilution of this lot detected DYNEIN on 10 μg of A431 lysates.
Descripción de destino
Forma física
Nota de análisis
HeLa cells, A431 cell lysate
Otras notas
Información legal
¿No encuentra el producto adecuado?
Pruebe nuestro Herramienta de selección de productos.
Opcional
Código de clase de almacenamiento
10 - Combustible liquids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 2
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico