17-10210
ProteoExtract® Native Cytoskeleton Enrichment
The ProteoExtract Native Cytoskeleton Enrichment & Staining Kit provides cytoskeleton purification detergent buffers that retain focal adhesion & actin-associated proteins while removing soluble cytoplasmic & nuclear proteins from the cell.
About This Item
Productos recomendados
Nivel de calidad
fabricante / nombre comercial
Chemicon®
ProteoExtract®
técnicas
immunocytochemistry: suitable
immunofluorescence: suitable
aplicaciones
sample preparation
Condiciones de envío
dry ice
Descripción general
http://www.nature.com/app_notes/nmeth/2012/121007/pdf/an8624.pdf
(Click Here!)
Rediscovering the Actin Cytoskeleton: New techniques leading to discoveries in cell migration, Dr. Richard Klemke, Morris Cancer Center, UCSD, USA.
The actin cytoskeleton is a highly dynamic network composed of actin polymers and a large variety of associated proteins. The functions of the actin cytoskeleton is to mediate a variety of essential biological functions in all eukaryotic cells, including intra- and extra-cellular movement and structural
Support (Chen, C.S., et al., 2003; Frixione E., 2000). To perform these functions, the organization of the actin cytoskeleton must be tightly regulated both temporally and spatially. Many proteins associated with the actin cytoskeleton are thus likely targets of signaling pathways controlling actin assembly. Actin cytoskeleton assembly is regulated at multiple levels, including the organization of actin monomers (G-actin) into actin polymers and the superorganization of actin polymers into a filamentous network (F-actin – the major constituent of microfilaments) (Bretscher, A., et al., 1994). This superorganization of actin polymers into a filamentous network is mediated by actin side-binding or cross-linking proteins (Dubreuil, R. R., 1991; Matsudaira, P., 1991; Matsudaira, P., 1994). The actin cytoskeleton is a dynamic structure that rapidly changes shape and organization in response to stimuli and cell cycle progression. Therefore, a disruption of its normal regulation may lead to cell transformations and cancer. Transformed cells have been shown to contain less F-actin than untransformed cells and exhibit atypical coordination of F-actin levels throughout the cell cycle (Rao, J.Y., et al., 1990). Orientational distribution of actin filaments within a cell is, therefore, an important determinant of cellular shape and motility.
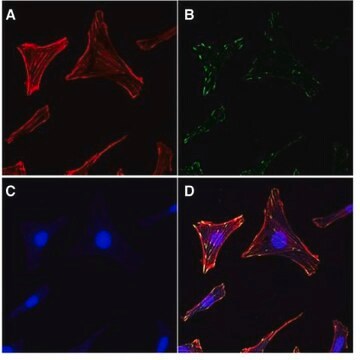
Focal adhesion and adherens junctions are membrane-associated complexes that serve as nucleation sites for actin filaments and as cross-linkers between the cell exterior, plasma membrane and actin cytoskeleton (Yamada, K.M., Geiger, B., 1997). The function of focal adhesions is structural, linking the ECM on the outside to the actin cytoskeleton on the inside. They are also sites of signal transduction, initiating signaling pathways in response to adhesion. Focal adhesions consist of integrin-type receptors that are attached to the extracellular matrix and are intracellularly associated with protein complexes containing vinculin (universal focal adhesion marker), talin, α-actinin, paxillin, tensin, zyxin and focal adhesion kinase (FAK) (Burridge, K., et al., 1990; Turner, C.E., Burridge, K., 1991).
Studying the proteins that associate with and regulate the actin cytoskeleton has been traditionally difficult because of the insolubility of the cytoskeleton in traditional detergents like Triton-X100. Work over the years has shown that many actin regulatory proteins/phospho-proteins upon activation move from the soluble cytoplasmic compartment to the insoluble actin cytoskeleton. The insolubility of these important proteins has made it difficult to study their biochemical changes, such as phosphorylation and nitrosylation, upon binding to actin. What is sorely needed is a cytoskeleton purification method that allows for the selective enrichment of cytoskeleton-associated proteins for detailed protein biochemical analyses. Such a method would provide the means to directly study this important pool of proteins in normal and diseased cytoskeletons.
Aplicación
Cell Structure
Cytoskeleton
Envase
Componentes
One bottle containing 3.5 mL of 20x Cytoskeleton Wash Buffer
One bottle containing 9 mL of ready to use Nuclear Extraction Buffer
One vial containing 100 µL of 1000x Protease Inhibitor Cocktail solution
One vial containing 150 µL of 1000x Sodium Orthovanadate solution
One vial containing 50 µL of 200x donkey anti-mouse FITC conjugate
One bottle containing 12.5 mL of 10x Blocking/Permeabilization Buffer
One vial containing 15 µg lyophilized TRITC-Conjugated Phalloidin
One vial containing 100 µL of 200x DAPI
One vial containing 100 µL of 100x anti-Vinculin mouse monoclonal IgG1 antibody
One vial containing 16 µL of 500x anti-GAPDH mouse monoclonal IgG1 antibody
Almacenamiento y estabilidad
Información legal
Cláusula de descargo de responsabilidad
Palabra de señalización
Danger
Frases de peligro
Consejos de prudencia
Clasificaciones de peligro
Acute Tox. 3 Dermal - Acute Tox. 3 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 3 Oral - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 1 - Eye Dam. 1 - Flam. Liq. 2 - Skin Corr. 1C - Skin Sens. 1 - STOT SE 1
Órganos de actuación
Eyes,Central nervous system
Código de clase de almacenamiento
3 - Flammable liquids
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
50.0 °F
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
10 °C
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Busque Certificados de análisis (COA) introduciendo el número de lote del producto. Los números de lote se encuentran en la etiqueta del producto después de las palabras «Lot» o «Batch»
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico