810142C
Avanti
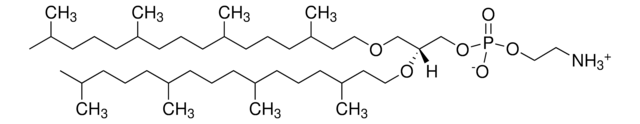
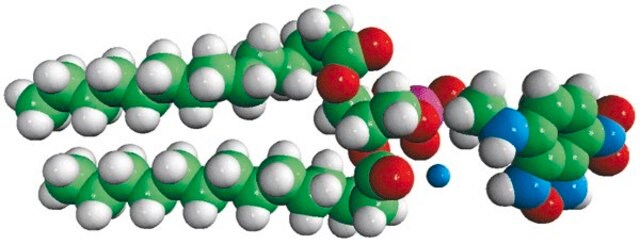
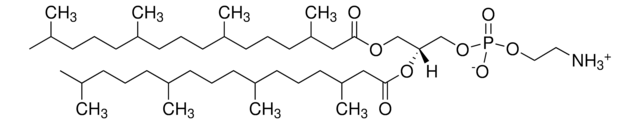
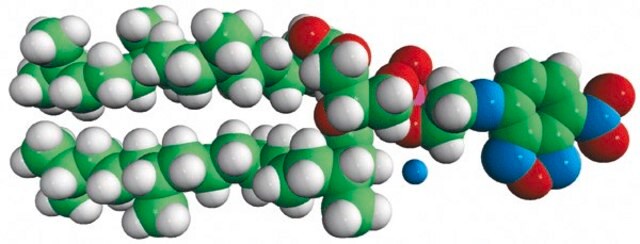
4ME 16:0 NBD PE (NBD-DPhPE)
1,2-diphytanoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine-N-(7-nitro-2-1,3-benzoxadiazol-4-yl) (ammonium salt), chloroform
Sinónimos:
NBD-DPhPE
About This Item
Productos recomendados
Ensayo
>99% (TLC)
Formulario
liquid
envase
pkg of 1 × 1 mL (810142C-1mg)
fabricante / nombre comercial
Avanti Research™ - A Croda Brand 810142C
concentración
1 mg/mL (810142C-1mg)
Condiciones de envío
dry ice
temp. de almacenamiento
−20°C
Descripción general
Aplicación
Envase
Información legal
Palabra de señalización
Danger
Frases de peligro
Consejos de prudencia
Clasificaciones de peligro
Acute Tox. 3 Inhalation - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Chronic 3 - Carc. 2 - Eye Irrit. 2 - Repr. 2 - Skin Irrit. 2 - STOT RE 1 - STOT SE 3
Órganos de actuación
Central nervous system, Liver,Kidney
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 3
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
Certificados de análisis (COA)
Lo sentimos, en este momento no disponemos de COAs para este producto en línea.
Si necesita más asistencia, póngase en contacto con Atención al cliente
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico