765112
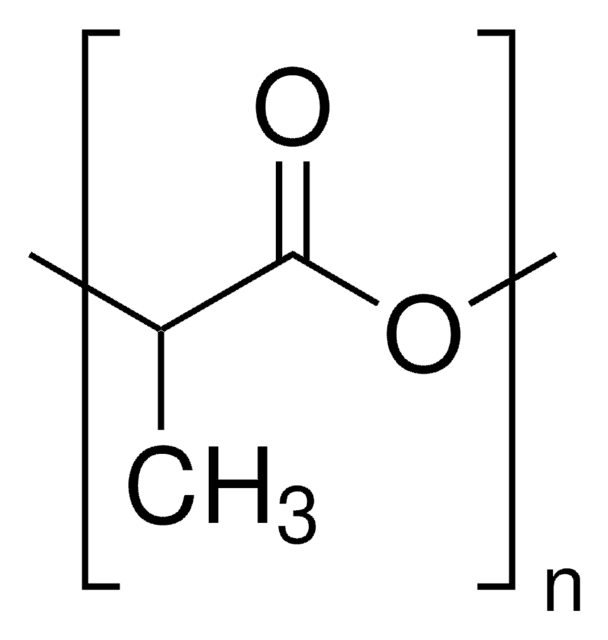
Poly(L-lactide)
average Mn 10,000, PDI ≤1.1
Sinónimos:
PLA, PLLA, Polylactide, L-Lactide polymer, PLA, Poly(L-Lactic acid)
About This Item
Productos recomendados
Formulario
solid
Nivel de calidad
actividad óptica
[α]22/D -150°, c = 0.5% in chloroform
mol peso
average Mn 10,000
marco temporal de la degradación
>3 years
temperatura de transición
Tm 162-167 °C
PDI
≤1.1
temp. de almacenamiento
2-8°C
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
Categorías relacionadas
Descripción general
Aplicación
Características y beneficios
Código de clase de almacenamiento
11 - Combustible Solids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Artículos
Professor Aran (Claremont University, USA) thoroughly discusses the engineering of graphene based materials through careful functionalization of graphene oxide, a solution processable form of graphene.
Local delivery of bioactive molecules using an implantable device can decrease the amount of drug dose required as well as non-target site toxicities compared to oral or systemic drug administration.
The world of commercial biomaterials has stagnated over the past 30 years as few materials have successfully transitioned from the bench to clinical use. Synthetic aliphatic polyesters have continued to dominate the field of resorbable biomaterials due to their long history and track record of approval with the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).
Microparticle drug delivery systems have been extensively researched and applied to a wide variety of pharmaceutical and medical applications due to a number of advantages including injectability, local applicability to target tissues and sites, and controlled drug delivery over a given time period.
Global Trade Item Number
| Número de referencia del producto (SKU) | GTIN |
|---|---|
| 765112-5G | 4061832923277 |
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico