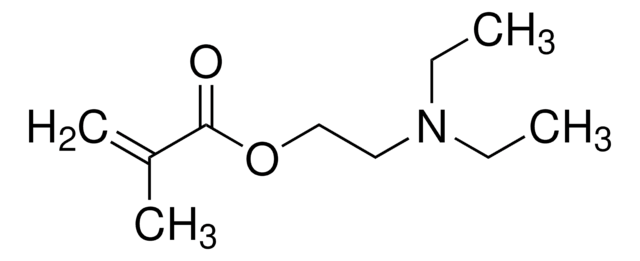
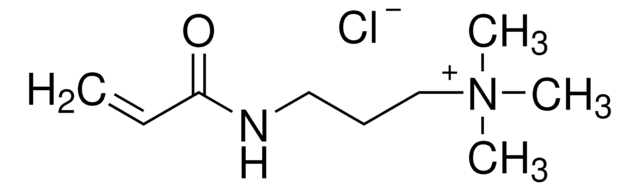
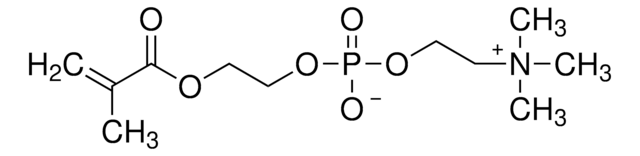
731099
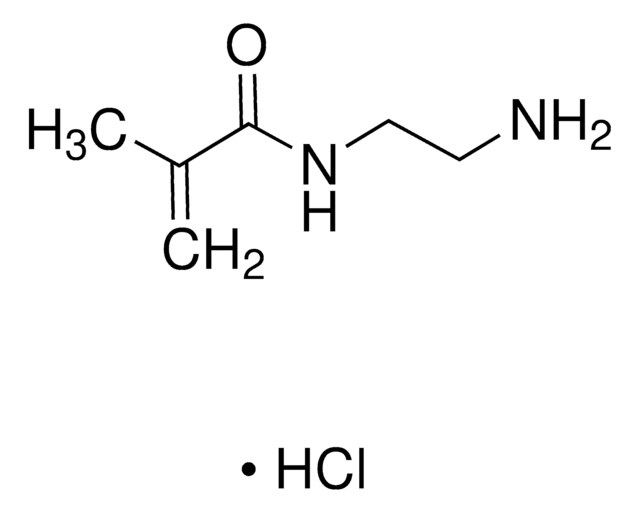
N-(3-Aminopropyl)methacrylamide hydrochloride
contains ≤1,000 ppm MEHQ as stabilizer, 98% (HPLC)
Sinónimos:
APMA
Iniciar sesiónpara Ver la Fijación de precios por contrato y de la organización
About This Item
Fórmula empírica (notación de Hill):
C7H14N2O · HCl
Número de CAS:
Peso molecular:
178.66
Número MDL:
Código UNSPSC:
12162002
ID de la sustancia en PubChem:
NACRES:
NA.23
Productos recomendados
Análisis
98% (HPLC)
formulario
powder
contiene
≤1,000 ppm MEHQ as stabilizer
mp
123-128 °C
temp. de almacenamiento
2-8°C
cadena SMILES
Cl.CC(=C)C(=O)NCCCN
InChI
1S/C7H14N2O.ClH/c1-6(2)7(10)9-5-3-4-8;/h1,3-5,8H2,2H3,(H,9,10);1H
Clave InChI
XHIRWEVPYCTARV-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Descripción general
N-(3-Aminopropyl)methacrylamide hydrochloride (APMA) is an aminoalkyl methacrylamide which can be synthesized by adding 1,3-diaminopropane to 1,3-diaminopropane dihydrogen chloride solution and further mixing the solution with methacrylic anhydride and hydroquinone. It has a primary amine that provides attractive features such as pH-responsiveness, affinity for anionic drugs and conjugation for variety of chemical structures.
Aplicación
APMA can be used in the preparation of copolymers and cross-linked miscellas for gene delivery, drug delivery and diagnostics applications.
Palabra de señalización
Warning
Frases de peligro
Consejos de prudencia
Clasificaciones de peligro
Eye Irrit. 2
Código de clase de almacenamiento
11 - Combustible Solids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Efficient RAFT polymerization of N-(3-aminopropyl) methacrylamide hydrochloride using unprotected ?clickable? chain transfer agents
Mendoncca PV, et al.
Reactive and Functional Polymers, 81(2), 1-7 (2014)
Facile synthesis of controlled-structure primary amine-based methacrylamide polymers via the reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer process
Deng Z, et al.
Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry, 46(15), 4984-4996 (2008)
Gaurasundar M Conley et al.
Nature communications, 10(1), 2436-2436 (2019-06-06)
Thermosensitive microgels are widely studied hybrid systems combining properties of polymers and colloidal particles in a unique way. Due to their complex morphology, their interactions and packing, and consequentially the viscoelasticity of suspensions made from microgels, are still not fully
Polymer mediated peptide immobilization onto amino-containing N-isopropylacrylamide-styrene core-shell particles
Rossi S, et al.
Colloid and Polymer Science, 282(3), 215-222 (2004)
Michika Onoda et al.
Nature communications, 8, 15862-15862 (2017-07-14)
In the field of polymer science, many kinds of polymeric material systems that show a sol-gel transition have been created. However, most systems are unidirectional stimuli-responsive systems that require physical signals such as a change in temperature. Here, we report
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico


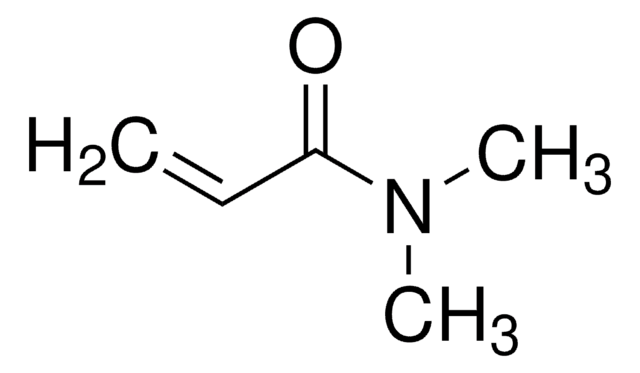
![N-[3-(Dimethylamino)propyl]methacrylamide 99%, contains MEHQ as inhibitor](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/295/145/6b4aae15-7cb5-4b7b-9c06-8e6d24e50951/640/6b4aae15-7cb5-4b7b-9c06-8e6d24e50951.png)

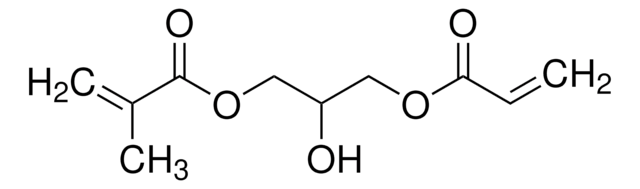
![[3-(Methacryloylamino)propyl]trimethylammonium chloride solution 50 wt. % in H2O](/deepweb/assets/sigmaaldrich/product/structures/189/736/089bc8ae-2a98-416d-9f9a-a0a510b6b828/640/089bc8ae-2a98-416d-9f9a-a0a510b6b828.png)