529265
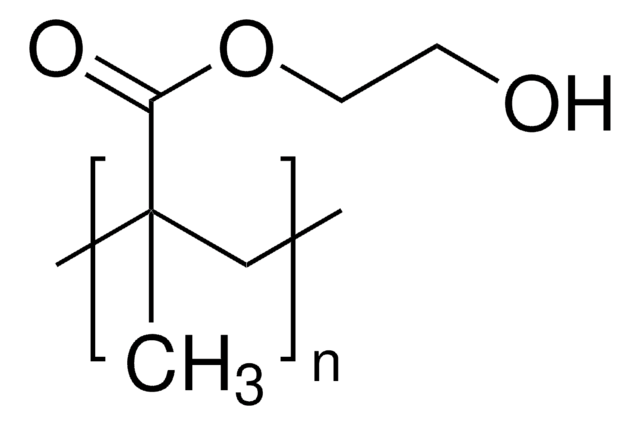
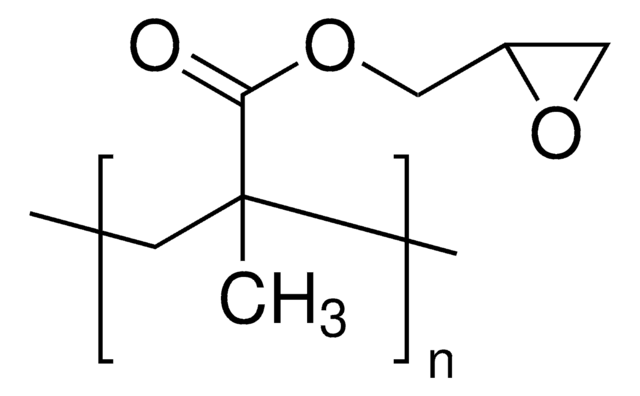
Poli(2-hidroxietil metacrilato)
average Mv 20,000
Sinónimos:
Poli (2-HEMA), Poli-HEMA
About This Item
Productos recomendados
formulario
powder
Nivel de calidad
mol peso
average Mv 20,000
temperatura de transición
Tg 84.8 °C
densidad
1.15 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
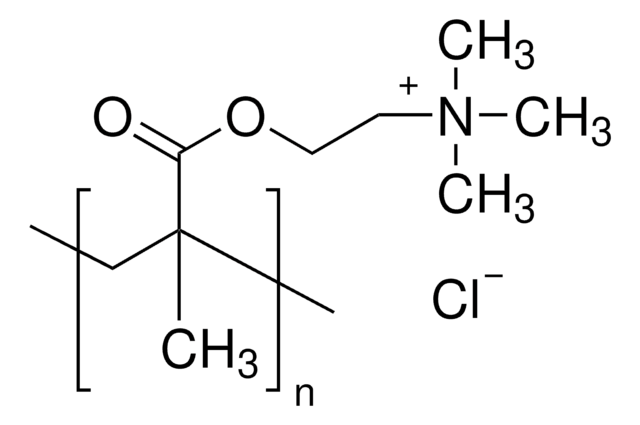
cadena SMILES
CC(=C)C(=O)OCCO
InChI
1S/C6H10O3/c1-5(2)6(8)9-4-3-7/h7H,1,3-4H2,2H3
Clave InChI
WOBHKFSMXKNTIM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
Aplicación
- Hydrogen-bonds structure in poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) studied by temperature-dependent infrared spectroscopy: Investigates the hydrogen-bond structure in poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) (PHEMA) using temperature-dependent IR spectroscopy. (S Morita, 2014).
- Transparent and tough poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) hydrogels prepared in water/IL mixtures: Describes the development of tough and transparent PHEMA hydrogels for potential use in various biomedical applications. (Y Liu et al., 2020).
- Reduced cell attachment to poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate)-coated ventricular catheters in vitro: Examines how PHEMA coatings can reduce cell attachment, which is beneficial for biomedical devices like catheters. (BW Hanak et al., 2018).
- Surface modification of poly(2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate) hydrogel for contact lens application: Studies modifications to PHEMA hydrogels to improve their suitability for contact lens applications. (M Kazemi Ashtiani, M Zandi, 2018).
Forma física
Código de clase de almacenamiento
11 - Combustible Solids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Equipo de protección personal
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Artículos
Professor Shrike Zhang (Harvard Medical School, USA) discusses advances in 3D-bioprinted tissue models for in vitro drug testing, reviews bioink selections, and provides application examples of 3D bioprinting in tissue model biofabrication.
Professor Shrike Zhang (Harvard Medical School, USA) discusses advances in 3D-bioprinted tissue models for in vitro drug testing, reviews bioink selections, and provides application examples of 3D bioprinting in tissue model biofabrication.
Self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) have attracted enormous interest for a wide variety of applications in micro- and nano-technology. In this article, we compare the benefits of three different classes of SAM systems (alkylthiolates on gold.
Biomaterials science involves the design and fabrication of smart materials for studying, directing, or mimicking biology. For successful integration of biomaterials in biological research, a meaningful understanding of biological systems is required.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico