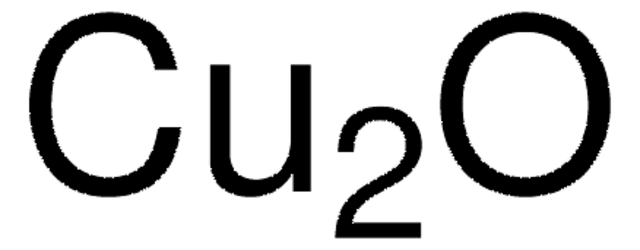342467
Copper(II) sulfide
powder, −100 mesh, ≥99% trace metals basis
Sinónimos:
Copper Blue, Copper monosulfide, Cupric sulfide, Horace Vernet′s Blue
Iniciar sesiónpara Ver la Fijación de precios por contrato y de la organización
About This Item
Fórmula empírica (notación de Hill):
CuS
Número de CAS:
Peso molecular:
95.61
Número CE:
Número MDL:
Código UNSPSC:
12352300
ID de la sustancia en PubChem:
NACRES:
NA.23
Productos recomendados
Nivel de calidad
Análisis
≥99% trace metals basis
formulario
powder
tamaño de partícula
−100 mesh
mp
220 °C (dec.) (lit.)
densidad
4.6 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
aplicaciones
battery manufacturing
cadena SMILES
S=[Cu]
InChI
1S/Cu.S
Clave InChI
BWFPGXWASODCHM-UHFFFAOYSA-N
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
Descripción general
Cu63 NMR, X ray photoelectron spectroscopy,2 copper sulfide CuS was studied in detail.
Envase
Packaged in glass bottles
Código de clase de almacenamiento
11 - Combustible Solids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Equipo de protección personal
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
K Pedersen
Journal of applied microbiology, 108(3), 1094-1104 (2009-12-18)
To investigate the relationships between sulfate-reducing bacteria (SRB), growth conditions, bentonite densities and copper sulfide generation under circumstances relevant to underground, high-level radioactive waste repositories. Experiments took place 450 m underground, connected under in situ pressure to groundwater containing SRB.
Qiwei Tian et al.
ACS nano, 5(12), 9761-9771 (2011-11-09)
Photothermal ablation (PTA) therapy has a great potential to revolutionize conventional therapeutic approaches for cancers, but it has been limited by difficulties in obtaining biocompatible photothermal agents that have low cost, small size (<100 nm), and high photothermal conversion efficiency.
Geng Ku et al.
ACS nano, 6(8), 7489-7496 (2012-07-21)
Photoacoustic tomography (PAT) is an emerging molecular imaging modality. Here, we demonstrate use of semiconductor copper sulfide nanoparticles (CuS NPs) for PAT with an Nd:YAG laser at a wavelength of 1064 nm. CuS NPs allowed visualization of mouse brain after
Wei Zhu et al.
Bioresource technology, 102(4), 3877-3882 (2011-01-05)
The sulfur oxidation activities of four pure thermophilic archaea Acidianus brierleyi (JCM 8954), Metallosphaera sedula (YN 23), Acidianus manzaensis (YN 25) and Sulfolobus metallicus (YN 24) and their mixture in bioleaching chalcopyrite were compared. Meanwhile, the relevant surface sulfur speciation
Caifeng Ding et al.
Biosensors & bioelectronics, 25(5), 1082-1087 (2009-10-27)
An ultrasensitive chemiluminescence method based on the Au nanoparticles amplification for the quantitative detection of single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in genomic DNA was accomplished by the DNA polymerase I (Klenow fragment)-induced coupling of the nucleotide-modified nanoparticle probe to the mutant sites
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico