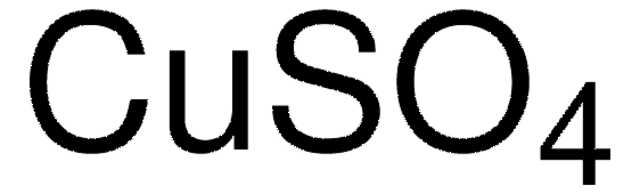203149
Copper(II) chloride
99.999% trace metals basis
Sinónimos:
Cupric chloride
About This Item
Productos recomendados
Análisis
99.999% trace metals basis
formulario
powder
idoneidad de la reacción
reagent type: catalyst
core: copper
impurezas
≤15.0 ppm Trace Metal Analysis
mp
620 °C (lit.)
densidad
3.386 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
aplicaciones
battery manufacturing
cadena SMILES
Cl[Cu]Cl
InChI
1S/2ClH.Cu/h2*1H;/q;;+2/p-2
Clave InChI
ORTQZVOHEJQUHG-UHFFFAOYSA-L
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
Descripción general
Aplicación
Palabra de señalización
Danger
Frases de peligro
Consejos de prudencia
Clasificaciones de peligro
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Oral - Aquatic Acute 1 - Aquatic Chronic 2 - Eye Dam. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2
Código de clase de almacenamiento
8A - Combustible corrosive hazardous materials
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Equipo de protección personal
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
Artículos
Noble-Metal Nanostructures with Controlled Morphologies
Oxidation and reduction reactions are some of the most common transformations encountered in organic synthesis
Thermoelectric Performance of Perovskite-type Oxide Materials
Spectral conversion for solar cells is an emerging concept in the field of photovoltaics, and it has the potential to increase significantly the efficiency of solar cells. Lanthanide ions are ideal candidates for spectral conversion, due to their high luminescence efficiencies and rich energy level structure that allows for great flexibility in the upconversion and downconversion of photons in a wide spectral region (NIR-VIS-UV).
Protocolos
We presents an article featuring procedures that describe polymerization of methyl methacrylate and vinyl acetate homopolymers and a block copolymer as performed by researchers at CSIRO.
Sigma-Aldrich presents an article about RAFT, or Reversible Addition/Fragmentation Chain Transfer, which is a form of living radical polymerization.
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico