177148
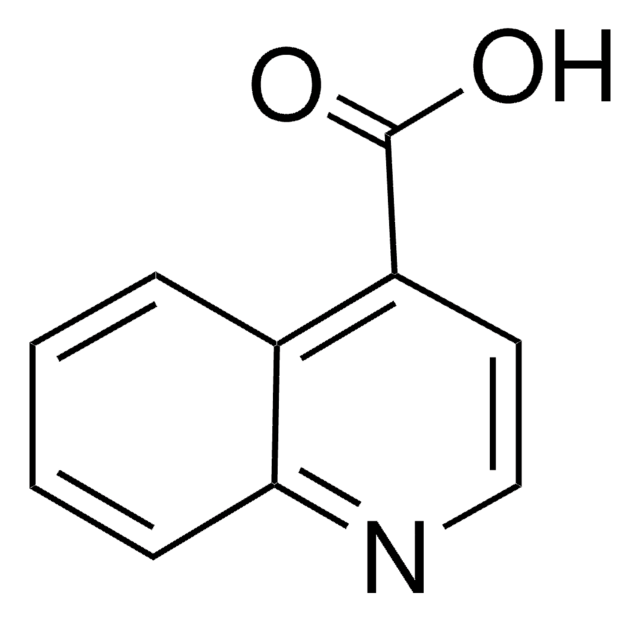
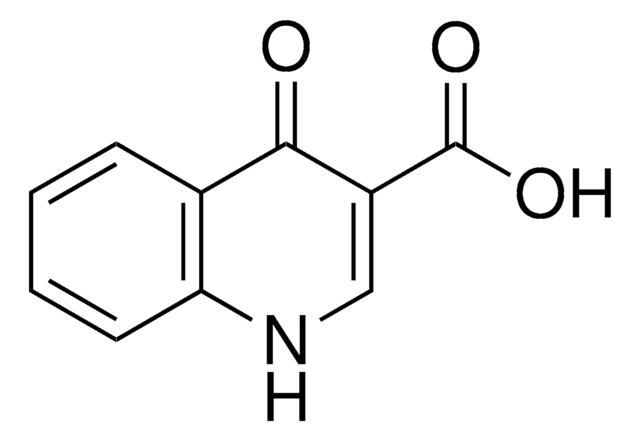
3-Quinolinecarboxylic acid
98%
Iniciar sesiónpara Ver la Fijación de precios por contrato y de la organización
About This Item
Fórmula empírica (notación de Hill):
C10H7NO2
Número de CAS:
Peso molecular:
173.17
Beilstein:
126542
Número CE:
Número MDL:
Código UNSPSC:
12352100
ID de la sustancia en PubChem:
NACRES:
NA.22
Productos recomendados
Nivel de calidad
Ensayo
98%
mp
277-280 °C (lit.)
grupo funcional
carboxylic acid
cadena SMILES
OC(=O)c1cnc2ccccc2c1
InChI
1S/C10H7NO2/c12-10(13)8-5-7-3-1-2-4-9(7)11-6-8/h1-6H,(H,12,13)
Clave InChI
DJXNJVFEFSWHLY-UHFFFAOYSA-N
¿Está buscando productos similares? Visita Guía de comparación de productos
Categorías relacionadas
Descripción general
The antibacterial activity of 3-quinolinecarboxylic acid derivatives were evaluated.
Código de clase de almacenamiento
11 - Combustible Solids
Clase de riesgo para el agua (WGK)
WGK 3
Punto de inflamabilidad (°F)
Not applicable
Punto de inflamabilidad (°C)
Not applicable
Equipo de protección personal
Eyeshields, Gloves, type N95 (US)
Elija entre una de las versiones más recientes:
¿Ya tiene este producto?
Encuentre la documentación para los productos que ha comprado recientemente en la Biblioteca de documentos.
Los clientes también vieron
M P Wentland et al.
Journal of medicinal chemistry, 27(9), 1103-1108 (1984-09-01)
A series of novel 3-quinolinecarboxylic acid derivatives have been prepared and their antibacterial activity evaluated. These derivatives are characterized by fluorine attached to the 6-position and substituted amino groups appended to the 1- and 7-positions. Structure-activity relationship studies indicate that
Antonello Mai et al.
Journal of medicinal chemistry, 49(23), 6897-6907 (2006-12-13)
Starting from a yeast phenotypic screening performed on 21 compounds, we described the identification of two small molecules (9 and 18) able to significantly reduce the S. cerevisiae cell growth, thus miming the effect of GCN5 deletion mutant. Tested on
Ximei Liang et al.
Ecotoxicology (London, England), 24(7-8), 1566-1573 (2015-04-22)
The presence of antibiotics including norfloxacin in the aquatic environment may cause adverse effects in non-target organisms. But the toxic mechanisms of fluoroquinolone to fish species are still not completely elucidated. Thus, it is essential to investigate the response of
Nuestro equipo de científicos tiene experiencia en todas las áreas de investigación: Ciencias de la vida, Ciencia de los materiales, Síntesis química, Cromatografía, Analítica y muchas otras.
Póngase en contacto con el Servicio técnico