P7119
PGO Enzyme Preparation
1 G capsules
Synonym(s):
Peroxidase - Glucose oxidase preparation
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
12352204
NACRES:
NA.54
Recommended Products
Quality Level
form
powder
solubility
H2O: soluble capsule/100 mL at 25 °C, clear, colorless (pH 6.95-7.05)
storage temp.
2-8°C
General description
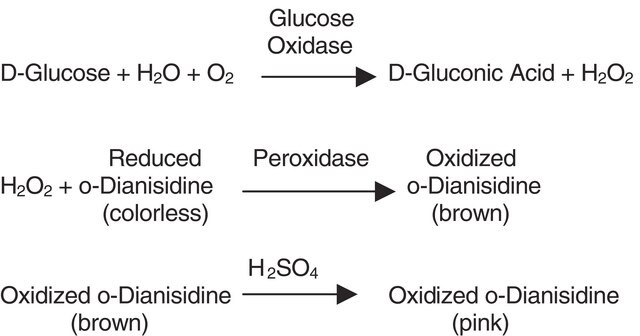
Each capsule contains 500 units of glucose oxidase (Aspergilus niger), 100 purpurogallin units of peroxidase (horseradish), and buffer salts. The reaction produces oxidized o-Dianisidine, which is brown. The intensity of the brown color measured at 425-475 nm is proportional to the original glucose concentration.
Application
PGO Enzymes preparation has been used:
- in diet sampling and chemical analyses
- to determine plasma and follicular fluid glucose levels
- to measure glucose content in fractions of retrograded debranched rice starch
Biochem/physiol Actions
PGO Enzymes are used for the quantitative, enzymatic determination of glucose in aqueous solutions such as serum. The reactions are normally monitored at 425-475 nm utilizing o-dianisidine as a colorimetric substrate. Glucose oxidase methods eliminate the effects of interfering substances. Contents of one capsule includes 100 units peroxidase and 500 units glucose oxidase and buffer salts.
Suitability
Tested and found suitable for use in the quantitation of glucose.
Preparation Note
The PGO enzymes solution is prepared by adding the contents of 1 capsule of PGO enzymes to 100 mL of water in an amber bottle. Bottle should be inverted several times with gentle shaking to dissolve. PGO Enzymes solution should be stored at 2-8 °C. The solution is stable for up to 1 month unless turbidity develops, and for at least 6 months at –20 °C.
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Resp. Sens. 1
Storage Class Code
13 - Non Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
G B Penner et al.
Journal of dairy science, 92(4), 1725-1733 (2009-03-25)
This study was conducted to determine the effects of feeding Fermenten (Church and Dwight Co., Princeton, NJ) with or without dietary sucrose on ruminal fermentation, apparent total-tract nutrient digestibility, and nutrient utilization. Eight ruminally cannulated Holstein cows (163 +/- 55
Risheng Ye et al.
Molecular metabolism, 5(7), 437-448 (2016-07-14)
Evidence hints at the ability of β-cells to emerge from non-β-cells upon genetic or pharmacological interventions. However, their quantitative contributions to the process of autonomous β-cell regeneration without genetic or pharmacological manipulations remain to be determined. Using PANIC-ATTAC mice, a
Roni Yair et al.
Journal of dairy science, 100(4), 2651-2659 (2017-01-31)
The objective of this study was to examine the effects of fructose and phosphate (Pi) infusions on dry matter intake by dairy cows to further understand the mechanisms controlling feed intake related to hepatic energy status. We performed 3 experiments
G B Penner et al.
Journal of dairy science, 92(7), 3341-3353 (2009-06-17)
The current study was undertaken to investigate the effect of feeding diets varying in sugar concentration to postpartum transition cows on productivity, ruminal fermentation, and nutrient digestibility. We hypothesized that the high-sugar diet would increase dry matter intake and lactation
Effect of dehydration methods on digested starch fractions of retrograded debranched rice starch
Boonna S, et al.
Journal of Science and Technology, 17(4), 359-368 (2010)
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service