P5145
Protein A–FITC from Staphylococcus aureus
essentially salt-free, lyophilized powder
Synonym(s):
Fluorescein isothiocyanate Protein A, Protein A–Fluorescein Isothiocyanate
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
MDL number:
UNSPSC Code:
12352203
Recommended Products
conjugate
FITC conjugate
Quality Level
form
essentially salt-free, lyophilized powder
extent of labeling
≥50 μg FITC per mg solid
technique(s)
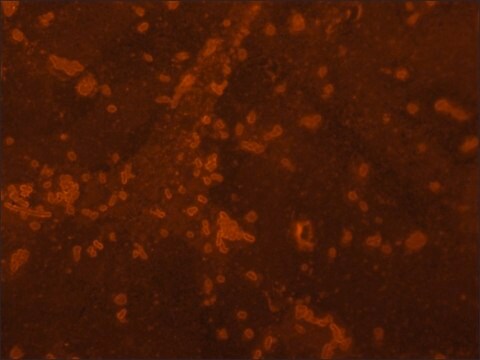
immunohistochemistry (frozen sections): 1:50 using human tonsil
capacity
≥4 mg/mg, solid binding capacity (human IgG)
storage temp.
2-8°C
Specificity
Binds IgG only from most mammals, except rat, goat, sheep.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Storage Class Code
13 - Non Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Assay for islet cell antibodies. Protein A--monoclonal antibody method.
Srikanta S et al
Diabetes, 34(3), 300-305 (1985)
P Henning et al.
Human gene therapy, 13(12), 1427-1439 (2002-09-07)
The use of adenovirus (Ad) as an efficient and versatile vector for in vivo tumor therapy requires the modulation of its cellular tropism. We previously developed a method to genetically alter the tropism of Ad5 fibers by replacing the fiber
spa typing method for discriminating among Staphylococcus aureus isolates: implications for use of a single marker to detect genetic micro- and macrovariation.
Koreen L et al
Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 42(2), 792-799 (2004)
A simple method for determining the labeling efficiency of fluorescein isothiocyanate products.
R M McKinney et al.
Analytical biochemistry, 14(3), 421-428 (1966-03-01)
Scott D Kobayashi et al.
mBio, 4(5), e00764-e00713 (2013-10-03)
Staphylococcus aureus is a prominent cause of human infections worldwide and is notorious for its ability to acquire resistance to antibiotics. Methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA), in particular, is endemic in hospitals and is the most frequent cause of community-associated bacterial
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service