O0382
Anti-Opioid δ Receptor antibody produced in rabbit
whole antiserum, lyophilized powder
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
biological source
rabbit
Quality Level
conjugate
unconjugated
antibody form
whole antiserum
antibody product type
primary antibodies
clone
polyclonal
form
lyophilized powder
mol wt
antigen ~55 kDa
species reactivity
mouse (predicted), rat
technique(s)
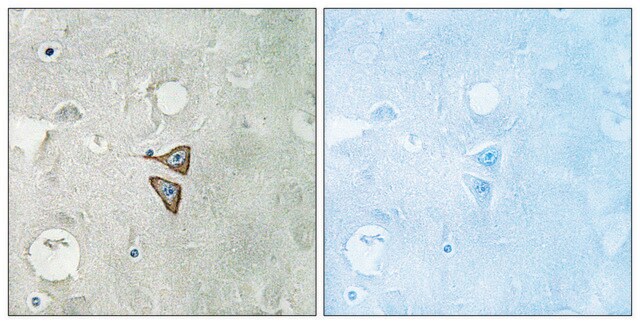
immunocytochemistry: 1:800 using PLP fixed rat brain sections
western blot: 1:800 using whole brain homogenate
UniProt accession no.
shipped in
wet ice
storage temp.
−20°C
Gene Information
mouse ... Oprd1(18386)
rat ... Oprd1(24613)
General description
Opioid peptides are endogenous neuromodulators that play a major role in nociception by interacting with several membrane receptors. Molecular cloning techniques have characterized the nucleotide sequence of several distinct opioid receptors, including the δ-, κ- and μ-opioid receptors.1 The cloned receptors are highly homologous (65%), differing only at the N- and C-termini and at the extracelluar loops that confer binding specificity. All three receptors interact with heterotrimeric G proteins.
δ-Opioid receptors (DOR) are located postsynaptically on pallidostriatal feedback neurons. DORs also modulate nociception presynaptically in the periaqueductal gray where immunolabeling of DOR has been shown to be intracellular and often associated with large dense-core vesicles. Additionally, receptor autoradiographic investigations have localized DORs to the external plexiform layer of the olfactory bulb, the nucleus accumbens, several layers of the cerebral cortex and several nuclei of the amygdala.
References
1. Goldstein, A. Trends Pharmacol. Sci., 8, 456-459 (1987).
δ-Opioid receptors (DOR) are located postsynaptically on pallidostriatal feedback neurons. DORs also modulate nociception presynaptically in the periaqueductal gray where immunolabeling of DOR has been shown to be intracellular and often associated with large dense-core vesicles. Additionally, receptor autoradiographic investigations have localized DORs to the external plexiform layer of the olfactory bulb, the nucleus accumbens, several layers of the cerebral cortex and several nuclei of the amygdala.
References
1. Goldstein, A. Trends Pharmacol. Sci., 8, 456-459 (1987).
Specificity
The antiserum is specific for the COOH terminal of the opioid δ receptor.
Immunogen
Peptide corresponding to the carboxy-terminal of the opioid δ receptor covalently attached onto a carrier protein.
Disclaimer
Unless otherwise stated in our catalog or other company documentation accompanying the product(s), our products are intended for research use only and are not to be used for any other purpose, which includes but is not limited to, unauthorized commercial uses, in vitro diagnostic uses, ex vivo or in vivo therapeutic uses or any type of consumption or application to humans or animals.
Not finding the right product?
Try our Product Selector Tool.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Personal Protective Equipment
dust mask type N95 (US), Eyeshields, Gloves
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
S R Childers
Life sciences, 48(21), 1991-2003 (1991-01-01)
Although pharmacological data provide strong evidence for different types of opioid receptors (e.g., mu, delta, and kappa), they share many common properties in their ability to couple to second messenger systems. All opioid receptor types are coupled to G-proteins, since
M F Olive et al.
The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 17(19), 7471-7479 (1997-09-20)
Parallel studies have demonstrated that enkephalin release from nerve terminals in the pallidum (globus pallidus and ventral pallidum) can be modulated by locally applied opioid drugs. To investigate further the mechanisms underlying these opioid effects, the present study examined the
The delta-opioid receptor: molecular pharmacology, signal transduction, and the determination of drug efficacy.
R M Quock et al.
Pharmacological reviews, 51(3), 503-532 (1999-09-02)
P A Zaki et al.
Annual review of pharmacology and toxicology, 36, 379-401 (1996-01-01)
Since the discovery of opioid receptors over two decades ago, an increasing body of work has emerged supporting the concept of multiple opioid receptors. Molecular cloning has identified three opioid receptor types--mu, delta, and kappa--confirming pharmacological studies that previously postulated
B L Kieffer
Cellular and molecular neurobiology, 15(6), 615-635 (1995-12-01)
1. Opioid peptides are a family of structurally related neuromodulators which play a major role in the control of nociceptive pathways. These peptides act through membrane receptors of the nervous system, defined as mu, delta and kappa and endowed with
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service