PHR1393
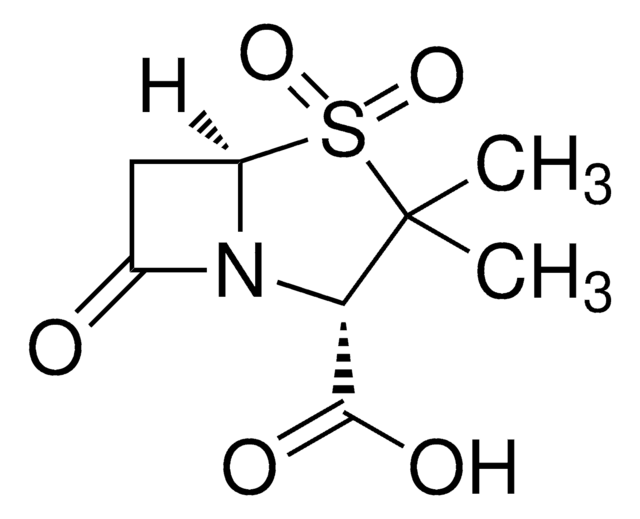
Ampicillin Trihydrate
Pharmaceutical Secondary Standard; Certified Reference Material
Synonym(s):
Ampicillin trihydrate, D-(−)-α-Aminobenzylpenicillin
About This Item
Recommended Products
grade
certified reference material
pharmaceutical secondary standard
Quality Level
Agency
traceable to BP 785
traceable to Ph. Eur. A1000000
traceable to USP 1033000/1033407
API family
ampicillin
CofA
current certificate can be downloaded
technique(s)
HPLC: suitable
gas chromatography (GC): suitable
mp
198-200 °C (dec.) (lit.)
application(s)
pharmaceutical (small molecule)
format
neat
storage temp.
2-8°C
SMILES string
O.O.O.CC1(C)S[C@@H]2[C@H](NC(=O)[C@H](N)c3ccccc3)C(=O)N2[C@H]1C(O)=O
InChI
1S/C16H19N3O4S.3H2O/c1-16(2)11(15(22)23)19-13(21)10(14(19)24-16)18-12(20)9(17)8-6-4-3-5-7-8;;;/h3-7,9-11,14H,17H2,1-2H3,(H,18,20)(H,22,23);3*1H2/t9-,10-,11+,14-;;;/m1.../s1
InChI key
RXDALBZNGVATNY-CWLIKTDRSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
General description
Application
Biochem/physiol Actions
Footnote
related product
Signal Word
Danger
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Eye Irrit. 2 - Resp. Sens. 1 - Skin Irrit. 2 - Skin Sens. 1 - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
It looks like we've run into a problem, but you can still download Certificates of Analysis from our Documents section.
If you need assistance, please contact Customer Support.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service