SCC148
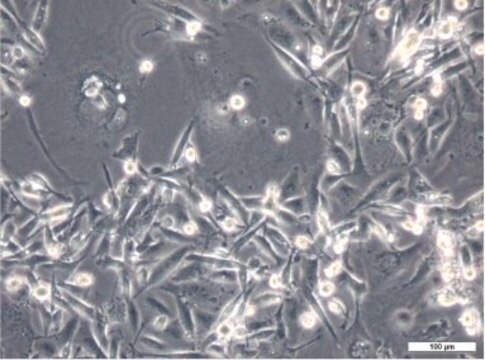
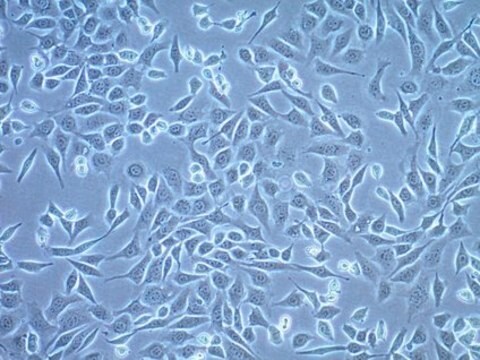
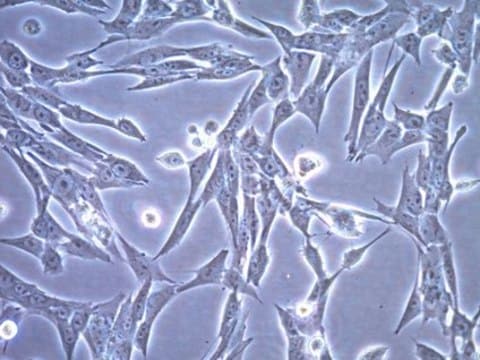
MB49 Mouse Bladder Carcinoma Cell Line
MB49 mouse urothelial carcinoma cell line is widely used as an in vitro and in vivo model of bladder cancer.
Synonym(s):
MB-49
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(2)
About This Item
UNSPSC Code:
41106514
eCl@ss:
32011203
NACRES:
NA.81
Recommended Products
biological source
mouse
Quality Level
technique(s)
cell culture | mammalian: suitable
shipped in
ambient
Related Categories
General description
MB49 cells are derived from C57BL/Icrf-a’ mouse bladder epithelial cells that were transformed by a single 24-hour treatment with the chemical carcinogen 7, 12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene (DMBA) on the second day of a long term primary culture . Transformed cells transplanted into syngeneic mice were shown to generate carcinomas . While of male origin, karyotype analyses indicate the loss of the Y chromosome in 100% of the cells analyzed . This abnormality is a frequent early event in human bladder cancer. A recent study indicates that MB49 cells recapitulate key features of sex differences in bladder tumor growth . MB49 implantation in mice resulted in significantly larger tumors in males than females. In the presence of dihydrotestosterone, MB49 cells exhibited enhanced proliferation in a dose-dependent manner. In contrast, MB49 cells were unresponsive to the pregnancy hormone, human chorionic gonadotrophin (hCG) . MB49 cells exhibit low to no expression of MHC-Class I and II molecules . However, upon exposure to IFN-, the expressions of MHC Class I and II are significantly upregulated .
Quality
• Each vial contains ≥ 1X106 viable cells.
• Cells are tested negative for infectious diseases by a Mouse Essential CLEAR panel by Charles River Animal Diagnostic Services.
• Cells are verified to be of mouse origin and negative for inter-species contamination from rat, chinese hamster, Golden Syrian hamster, human and non-human primate (NHP) as assessed by a Contamination CLEAR panel by Charles River Animal Diagnostic Services.
• Cells are negative for mycoplasma contamination
• Cells are tested negative for infectious diseases by a Mouse Essential CLEAR panel by Charles River Animal Diagnostic Services.
• Cells are verified to be of mouse origin and negative for inter-species contamination from rat, chinese hamster, Golden Syrian hamster, human and non-human primate (NHP) as assessed by a Contamination CLEAR panel by Charles River Animal Diagnostic Services.
• Cells are negative for mycoplasma contamination
Other Notes
This product is intended for sale and sold solely to academic institutions for internal academic research use per the terms of the "Academic Use Agreement" as detailed in the product documentation. For information regarding any other use, please contact licensing@emdmillipore.com.
Storage Class Code
10 - Combustible liquids
WGK
WGK 2
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
I C Summerhayes et al.
Journal of the National Cancer Institute, 62(4), 1017-1023 (1979-04-01)
Neoplastic transformation of C57BL/lcrf-a' mouse bladder epithelium was induced in long-term primary cultures by a single 24-hour treatment with 7,12-dimethylbenz[a]anthracene on day 2 of culture. Transformed foci appeared earlier (40--60 days) and at a higher frequency (28%) in cultures from
Shai White-Gilbertson et al.
Bladder (San Francisco, Calif.), 3(1) (2016-03-22)
The MB49 syngeneic, murine model of bladder cancer has been widely used for more than 35 years. In humans, bladder cancer is one third as prevalent in women as in men, with a trend toward lower prevalence in parous compared
Andreja Erman et al.
International journal of molecular sciences, 22(12) (2021-07-03)
Non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer is the most common form of bladder cancer. The main problem in managing bladder tumors is the high recurrence after the transurethral resection of bladder tumors (TURBT). Our study aimed to examine the fate of intravesically applied
Pietro Strobbia et al.
Theranostics, 11(9), 4090-4102 (2021-03-24)
For the majority of cancer patients, surgery is the primary method of treatment. In these cases, accurately removing the entire tumor without harming surrounding tissue is critical; however, due to the lack of intraoperative imaging techniques, surgeons rely on visual
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service