719854
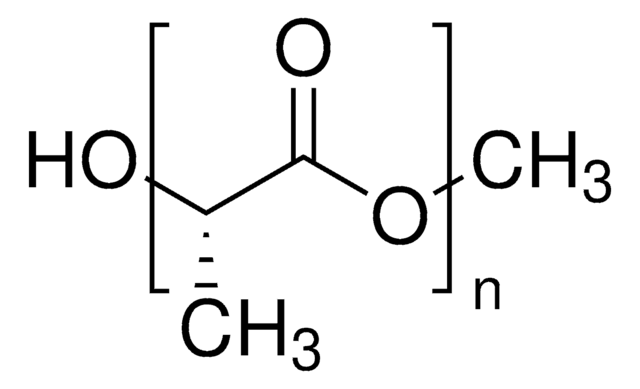
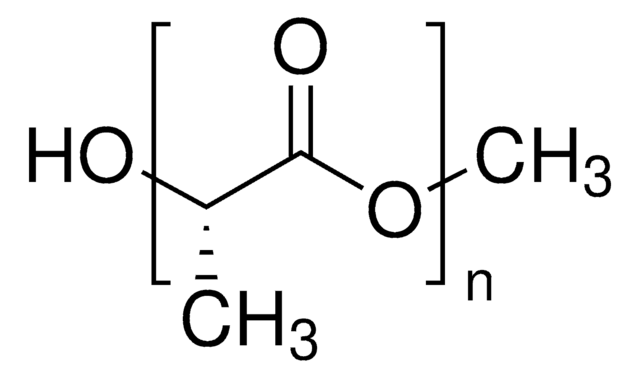
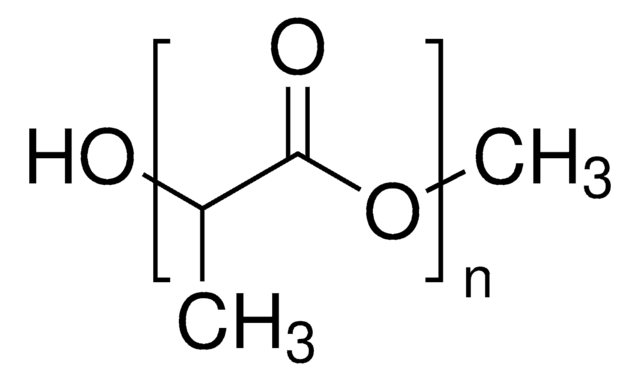
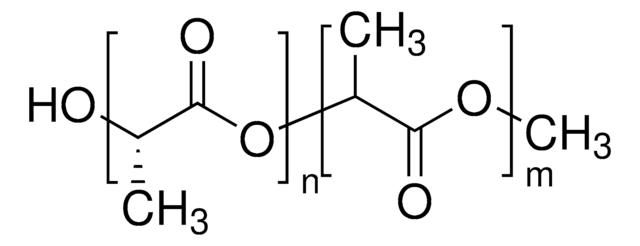
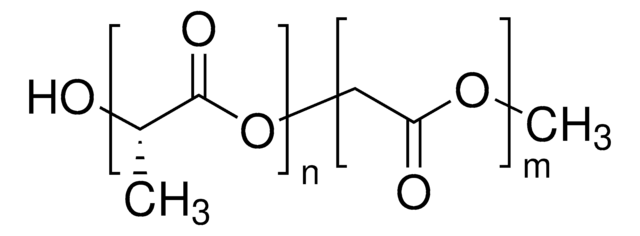
Resomer® L 206 S, Poly(L-lactide), ester terminated
Synonym(s):
PLL
About This Item
Recommended Products
form
granular
degradation timeframe
>3 years
viscosity
0.8-1.2 dL/g, 0.1 % in chloroform(25 °C, Ubbelohde) (size 0c glass capillary viscometer)
transition temp
Tm 180-185 °C
Tg 60-65 °C
storage temp.
2-8°C
General description
Application
Legal Information
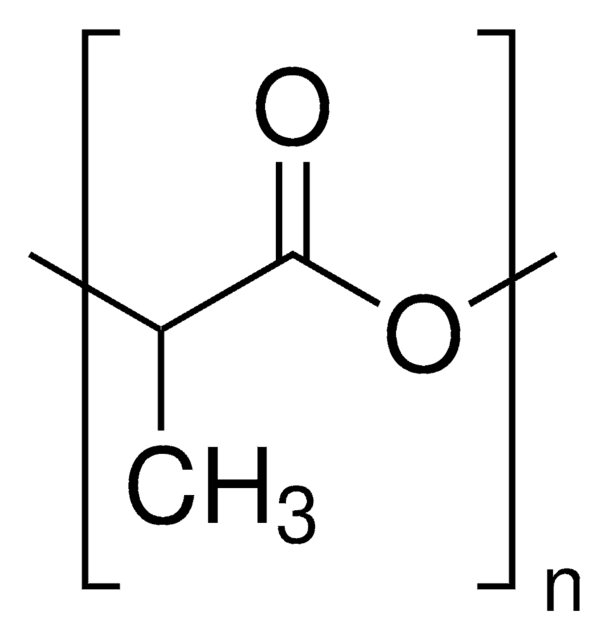
related product
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Certificates of Analysis (COA)
Search for Certificates of Analysis (COA) by entering the products Lot/Batch Number. Lot and Batch Numbers can be found on a product’s label following the words ‘Lot’ or ‘Batch’.
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
Aliphatic polyesters such as polylactide, poly(lactide-co-glycolide) and polycaprolactone, as well as their copolymers, represent a diverse family of synthetic biodegradable polymers that have been widely explored for medical uses and are commercially available.
Aliphatic polyesters such as polylactide, poly(lactide-co-glycolide) and polycaprolactone, as well as their copolymers, represent a diverse family of synthetic biodegradable polymers that have been widely explored for medical uses and are commercially available.
In the past two decades, tissue engineering and regenerative medicine have become important interdisciplinary fields that span biology, chemistry, engineering, and medicine.
Innovations in polymer technology have had a significant impact on the advancement of novel drug delivery systems.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service