234923
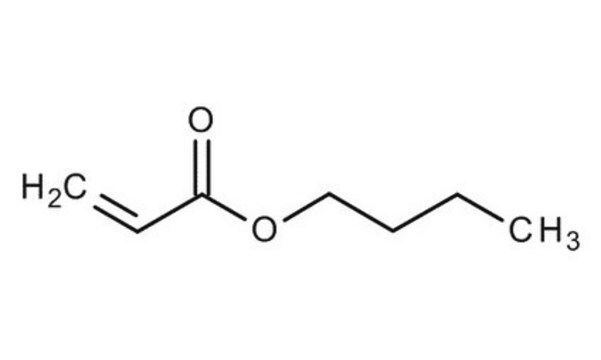
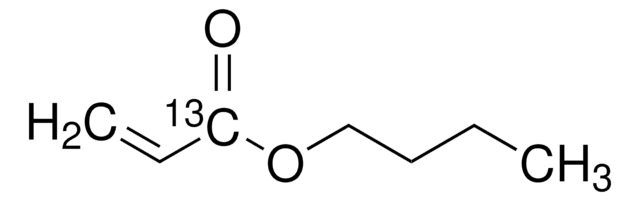
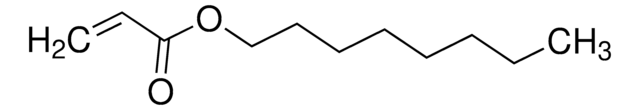
Butyl acrylate
≥99%, contains 10-60 ppm monomethyl ether hydroquinone as inhibitor
Synonym(s):
n-Butyl acrylate
About This Item
Recommended Products
vapor density
>1 (vs air)
Quality Level
vapor pressure
3.3 mmHg ( 20 °C)
Assay
≥99%
form
liquid
autoignition temp.
559 °F
contains
10-60 ppm monomethyl ether hydroquinone as inhibitor
expl. lim.
9.9 %
refractive index
n20/D 1.418 (lit.)
bp
145 °C (lit.)
density
0.894 g/mL at 25 °C (lit.)
SMILES string
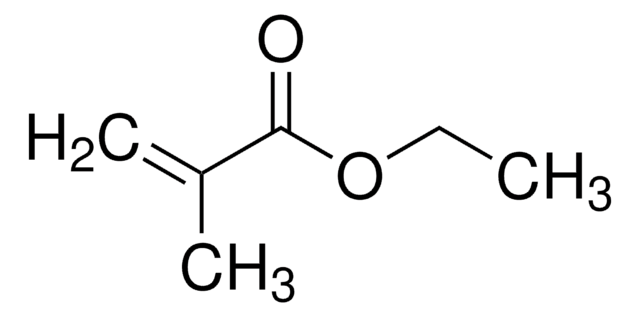
CCCCOC(=O)C=C
InChI
1S/C7H12O2/c1-3-5-6-9-7(8)4-2/h4H,2-3,5-6H2,1H3
InChI key
CQEYYJKEWSMYFG-UHFFFAOYSA-N
Looking for similar products? Visit Product Comparison Guide
Related Categories
General description
Butyl acrylate undergoes radical copolymerization with benzoxazine containing a vinyl group to afford copolymers. Heck coupling reactions of aryl bromides with n-butyl acrylate mediated by phosphine-imidazolium salt have been reported. Copolymerization of styrene and n-butyl acrylate by ATRP catalyzed by CuBr/4,4′-di(5-nonyl)-2,2′-bipyridine has been described.
Application
- An electrolyte additive in lithium-ion batteries to improve their low-temperature performance. The addition of BA to the electrolyte led to a significant improvement in the low-temperature performance of the battery, including enhanced ionic conductivity and improved rate capability.
- A monomer to synthesize a shape memory polymer network that contains magnetic nanoparticles for various applications, including actuators and biomedical devices.
- A monomer for the preparation of a polymeric semiconductor with intrinsically stretchable properties. This polymer material is used as a component in field-effect transistor applications.
- Poly(butyl acrylate) particles.
- Poly(butyl acrylate-b-acrylic acid) block copolymer.
- Amphiphilic charged diblock copolymers poly(butyl acrylate)-b-poly(acrylic acid).
- Poly(n-butyl acrylate), via atom transfer radical polymerization (ATRP) of n-butyl acrylate in the presence of CuIBr/4,4′-di(5-nonyl)-2,2′-bipyridine (catalyst).
Signal Word
Warning
Hazard Statements
Precautionary Statements
Hazard Classifications
Acute Tox. 4 Dermal - Acute Tox. 4 Inhalation - Aquatic Chronic 3 - Eye Irrit. 2 - Flam. Liq. 3 - Skin Irrit. 2 - Skin Sens. 1 - STOT SE 3
Target Organs
Respiratory system
Storage Class Code
3 - Flammable liquids
WGK
WGK 1
Flash Point(F)
98.6 °F - closed cup
Flash Point(C)
37 °C - closed cup
Personal Protective Equipment
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
Articles
The manufacture of monomers for use in ophthalmic applications is driven by the need for higher purity, improved reliability of manufacturing supply, but ultimately by the need for the increased comfort, convenience, and safety of contact lens wearers. Daily wear contact lenses have the potential to fill this need for many customers; however, their widespread use is constrained by higher costs compared to weekly- or monthly-based lenses. New approaches that improve cost structure and result in higher quality raw materials are needed to help make contact lenses more affordable and accelerate growth of the contact lens market.
The Heck reaction is the palladium catalyzed cross-coupling reaction between alkenes and aryl or vinyl halides (or triflates) to afford substituted alkenes.
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service