M8284
Maltose Phosphorylase from Enterococcus sp.
recombinant, expressed in E. coli, lyophilized powder
Synonym(s):
Maltose:orthophosphate 1-β-D-Glucosyltransferase
Sign Into View Organizational & Contract Pricing
All Photos(1)
About This Item
Recommended Products
recombinant
expressed in E. coli
Quality Level
form
lyophilized powder
specific activity
≥9 units/mg solid
mol wt
90 kDa by SDS-PAGE
storage temp.
−20°C
InChI
1S/C14H28O2/c1-2-3-4-5-6-7-8-9-10-11-12-13-14(15)16/h2-13H2,1H3,(H,15,16)
Related Categories
General description
Maltose phosphorylase (MP) is a dimeric enzyme. This enzyme is classified under family 65 of the glycoside hydrolases. It is a member of the disaccharide phosphorylase family.
Application
Maltose Phosphorylase from Enterococcus sp. has been used as a component in coupled assay and ATPase activity assay to study its effects on ATPase activity, on the 90 kDa heat shock proteins (Hsp90) ATPase reaction and on background absorbance on the production of resorufin.
Maltose phosphorylase from Enterococcus has been used in a study to describe a new pathway for maltose utilization in lactic acid bacteria. It has also been used in a study to describe the transfer of glucosyl moiety of maltose to acceptors with alcoholic OH groups.
Biochem/physiol Actions
Maltose phosphorylase (MP) is a dimeric enzyme that catalyzes maltose and inorganic phosphate into β-D-glucose-1-phosphate and glucose.
Maltose phosphorylase not only transfers glucosyl moieties from maltose to other sugars but has been shown to also use phenolic compounds such as salicyl alcohol as acceptors.
Enzymatically converts maltose to D-Glucose.
Unit Definition
One unit will produce 1.0 μmole of D-Glucose from maltose per minute at pH 7.0 at 30°C.
Other Notes
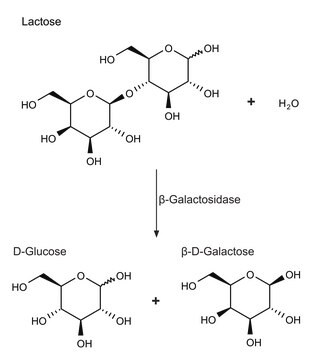
Contains lactose.
Storage Class Code
11 - Combustible Solids
WGK
WGK 3
Flash Point(F)
Not applicable
Flash Point(C)
Not applicable
Choose from one of the most recent versions:
Already Own This Product?
Find documentation for the products that you have recently purchased in the Document Library.
Customers Also Viewed
M P Egloff et al.
Structure (London, England : 1993), 9(8), 689-697 (2001-10-06)
Maltose phosphorylase (MP) is a dimeric enzyme that catalyzes the conversion of maltose and inorganic phosphate into beta-D-glucose-1-phosphate and glucose without requiring any cofactors, such as pyridoxal phosphate. The enzyme is part of operons that are involved in maltose/malto-oligosaccharide metabolism.
U Nilsson et al.
Microbiology (Reading, England), 147(Pt 6), 1565-1573 (2001-06-08)
Maltose phosphorylase (MP) from Lactococcus lactis was purified and the corresponding gene was cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli. The isoelectric point of the pure enzyme was determined to be 7.0. According to zymogram analysis and SDS-PAGE, the native MP
M Tangney et al.
FEMS microbiology letters, 76(1-2), 191-196 (1992-10-01)
Extracts prepared from cultures of Bacillus subtilis, grown on maltose as the sole carbon source, lacked maltose phosphotransferase system activity. There was, however, evidence for a maltose phosphorylase activity, and such extracts also possessed both glucokinase and glucose phosphotransferase system
Hiroyuki Nakai et al.
Carbohydrate research, 345(8), 1061-1064 (2010-04-16)
Lactobacillus acidophilus NCFM maltose phosphorylase (LaMalP) of glycoside hydrolase family 65 catalysed enzymatic synthesis of alpha-(1-->4)-glucosidic disaccharides from maltose and five monosaccharides in a coupled phosphorolysis/reverse phosphorolysis one-pot reaction. Thus phosphorolysis of maltose to beta-glucose 1-phosphate circumvented addition of costly
Y Le Breton et al.
Journal of applied microbiology, 98(4), 806-813 (2005-03-09)
The aim of this research was to characterize the metabolic pathway for maltose utilization in Enterococcus faecalis. Screening a library of Enterococcus faecalis insertional mutants allowed the isolation of mutants affected in maltose utilization. Genetic analysis of the insertion loci
Our team of scientists has experience in all areas of research including Life Science, Material Science, Chemical Synthesis, Chromatography, Analytical and many others.
Contact Technical Service